Update on imaging-based diagnosis of acute renal allograft rejection
- PMID: 31139495
- PMCID: PMC6526365
Update on imaging-based diagnosis of acute renal allograft rejection
Abstract
Kidney transplantation is the preferred treatment for patients with end-stage renal disease. Despite effective immunosuppressants, acute allograft rejections pose a major threat to graft survival. In early stages, acute rejections are still potentially reversible, and early detection is crucial to initiate the necessary treatment options and to prevent further graft dysfunction or even loss of the complete graft. Currently, invasive core needle biopsy is the reference standard to diagnose acute rejection. However, biopsies carry the risk of graft injuries and cannot be immediately performed on patients receiving anticoagulation drugs. Therefore, non-invasive assessment of the whole organ for specific and rapid detection of acute allograft rejection is desirable. We herein provide a review summarizing current imaging-based approaches for non-invasive diagnosis of acute renal allograft rejection.
Keywords: Acute allograft rejection; MRI; PET; SPECT; imaging; kidney transplantation; noninvasive; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
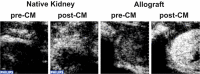
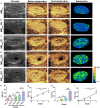
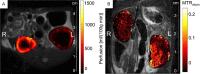
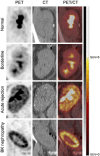
Figures

References
-
- Wolfe RA, Ashby VB, Milford EL, Ojo AO, Ettenger RE, Agodoa LY, Held PJ, Port FK. Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1725–1730. - PubMed
-
- Elbadri A, Traynor C, Veitch JT, O’Kelly P, Magee C, Denton M, O’Sheaghdha C, Conlon PJ. Factors affecting eGFR 5-year post-deceased donor renal transplant: analysis and predictive model. Ren Fail. 2015;37:417–423. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
