A method to implement continuous characters in digital identification keys that estimates the probability of an annotation
- PMID: 31139513
- PMCID: PMC6526653
- DOI: 10.1002/aps3.1247
A method to implement continuous characters in digital identification keys that estimates the probability of an annotation
Abstract
Premise: Species identification is vital to many disciplines. Digital technology has improved identification tools, but the direct use of characters with continuous states has yet to be fully realized. To achieve full use of continuous characters for identification, I propose a classifier that calculates a posterior probability (degree of belief) in possible name assignments and an estimate of the relative evidence for the candidate annotations.
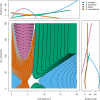
Methods: A model for a species is defined using continuous morphological characters, and an algorithm for identification with a naive Bayesian classifier, using the model, is presented. A method of estimating the strength of evidence for candidate species is also described.
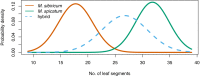
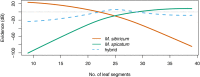
Results: The proposed method is applied in two example identifications: native vs. invasive Myriophyllum in North America and vegetative Rhipidocladum bamboos in Mexico. In each instance, the new method provides a probability and estimate of the strength of the probability to enhance the name assignment in situations where taxa are difficult to differentiate using discrete character states.
Discussion: Naive Bayesian classifiers take advantage of the predictive information inherent in continuous morphological characters. Application of this methodology to plant taxonomy advances our ability to leverage digital technology for improved interactive taxonomic identifications.
Keywords: continuous; identification; key; morphology; naive Bayesian classifier.
Figures


References
-
- Barrows, C. W. , Murphy‐Mariscal M. L., and Hernandez R. R.. 2016. At a crossroads: The nature of natural history in the twenty‐first century. BioScience 66: 592–599.
-
- Beers, R. J. , and Lockhart W. R.. 1962. Experimental methods in computer taxonomy. Journal of General Microbiology 28: 633–640. - PubMed
-
- Chang, W. , Cheng J., Allaire J. J., Xie Y., and McPherson J.. 2018. shiny: Web application framework for R. R package version 1.2.0. Website https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=shiny; [accessed 21 January 2019].
-
- Clark, L. G. , Londoño X., and Ruiz‐Sanchez E.. 2015. Bamboo taxonomy and habitat In Liese W. and Köhl M. [eds.], Bamboo: The plant and its uses, 1–30. Springer, Cham, Switzerland.
-
- Coffey, B. T. , and McNabb C. D.. 1974. Eurasian water‐milfoil in Michigan. Michigan Botanist 13: 159–165.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

