Impact of combination immunochemotherapies on progression of 4NQO-induced murine oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 31139925
- PMCID: PMC10577812
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-019-02348-2
Impact of combination immunochemotherapies on progression of 4NQO-induced murine oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
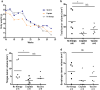
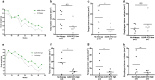
Advanced oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC) have limited therapeutic options. Although immune therapies are emerging as a potentially effective alternative or adjunct to chemotherapies, the therapeutic efficacy of combination immune chemotherapies has yet to be determined. Using a 4-nitroquinolone-N-oxide (4NQO) orthotopic model of OSCC in immunocompetent mice, we evaluated the therapeutic efficacy of single- and combined-agent treatment with a poly-epitope tumor peptide vaccine, cisplatin and/or an A2AR inhibitor, ZM241385. The monotherapies or their combinations resulted in a partial inhibition of tumor growth and, in some cases, a significant but transient upregulation of systemic anti-tumor CD8+ T cell responses. These responses eroded in the face of expanding immunoregulatory cell populations at later stages of tumor progression. Our findings support the need for the further development of combinatorial therapeutic approaches that could more effectively silence dominant immune inhibitory pathways operating in OSCC and provide novel, more beneficial treatment options for this tumor.
Keywords: 4NQO model; A2AR inhibition; Carcinogenesis; Chemotherapy; Oral squamous cell carcinoma; Vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Establishment of syngeneic murine model for oral cancer therapy.Oral Oncol. 2019 Aug;95:194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2019.06.026. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Oral Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31345390
-
Partial versus whole tumor-volume irradiation in combination with immunotherapy: Comparable outcomes in immunosuppressed mouse models of oral squamous cell carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2025 Jun;187:118107. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118107. Epub 2025 Apr 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2025. PMID: 40288172
-
4NQO induced carcinogenesis: A mouse model for oral squamous cell carcinoma.Methods Cell Biol. 2021;163:93-111. doi: 10.1016/bs.mcb.2021.01.001. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Methods Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33785171
-
Personalized cancer vaccination in head and neck cancer.Cancer Sci. 2021 Mar;112(3):978-988. doi: 10.1111/cas.14784. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33368875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond conventional chemotherapy, targeted therapy and immunotherapy in squamous cell cancer of the oral cavity.Oral Oncol. 2020 Jun;105:104673. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104673. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Oral Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32272385 Review.
Cited by
-
Nano-drug delivery system targeting FAP for the combined treatment of oral leukoplakia.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024 Jan;14(1):247-265. doi: 10.1007/s13346-023-01397-6. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 37526880
-
Genomic and Transcriptomic Landscape of an Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mouse Model for Immunotherapy.Cancer Immunol Res. 2023 Nov 1;11(11):1553-1567. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-23-0133. Cancer Immunol Res. 2023. PMID: 37669022 Free PMC article.
-
Polypodium leucotomos targets multiple aspects of oral carcinogenesis and it is a potential antitumor phytotherapy against tongue cancer growth.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 5;13:1098374. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1098374. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36686704 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse Tumor-Bearing Models as Preclinical Study Platforms for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2020 Feb 25;10:212. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00212. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32158692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting oral tumor microenvironment for effective therapy.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 May 23;23(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02943-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37221555 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

