Evolution of Mechanisms that Control Mating in Drosophila Males
- PMID: 31141679
- PMCID: PMC6646047
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.04.104
Evolution of Mechanisms that Control Mating in Drosophila Males
Abstract
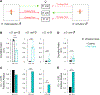
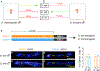
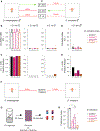
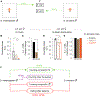
Genetically wired neural mechanisms inhibit mating between species because even naive animals rarely mate with other species. These mechanisms can evolve through changes in expression or function of key genes in sensory pathways or central circuits. Gr32a is a gustatory chemoreceptor that, in D. melanogaster, is essential to inhibit interspecies courtship and sense quinine. Similar to D. melanogaster, we find that D. simulans Gr32a is expressed in foreleg tarsi, sensorimotor appendages that inhibit interspecies courtship, and it is required to sense quinine. Nevertheless, Gr32a is not required to inhibit interspecies mating by D. simulans males. However, and similar to its function in D. melanogaster, Ppk25, a member of the Pickpocket family, promotes conspecific courtship in D. simulans. Together, we have identified distinct evolutionary mechanisms underlying chemosensory control of taste and courtship in closely related Drosophila species.
Keywords: Gr32a; Gr33a; Ppk25; chemosensation; courtship; evolution; mating; pheromones; reproduction; reproductive isolation.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Allaire JJ, Cheng J, Xie Y, McPherson J, Chang W, Allen J, Wickham H, Atkins A, Hyndman R, and Arslan R (2017). rmarkdown: Dynamic Documents for R https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/rmarkdown/index.html.
-
- Bastock M, and Manning A (1955). The courtship of Drosophila melanogaster. Behaviour 8, 85–111.
-
- Billeter J-C, Atallah J, Krupp JJ, Millar JG, and Levine JD (2009). Specialized cells tag sexual and species identity in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature 461, 987–991. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

