The role of m6A RNA methylation in human cancer
- PMID: 31142332
- PMCID: PMC6540575
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-019-1033-z
The role of m6A RNA methylation in human cancer
Abstract
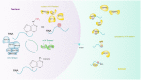
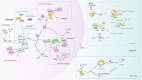
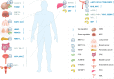
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is identified as the most common, abundant and conserved internal transcriptional modification, especially within eukaryotic messenger RNAs (mRNAs). M6A modification is installed by the m6A methyltransferases (METTL3/14, WTAP, RBM15/15B and KIAA1429, termed as "writers"), reverted by the demethylases (FTO and ALKBH5, termed as "erasers") and recognized by m6A binding proteins (YTHDF1/2/3, IGF2BP1 and HNRNPA2B1, termed as "readers"). Acumulating evidence shows that, m6A RNA methylation has an outsize effect on RNA production/metabolism and participates in the pathogenesis of multiple diseases including cancers. Until now, the molecular mechanisms underlying m6A RNA methylation in various tumors have not been comprehensively clarified. In this review, we mainly summarize the recent advances in biological function of m6A modifications in human cancer and discuss the potential therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Cancer; Growth; Metastasis; N6-methyladenosine; Prognosis; RNA methylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

