The Highly Recurrent PP2A Aα-Subunit Mutation P179R Alters Protein Structure and Impairs PP2A Enzyme Function to Promote Endometrial Tumorigenesis
- PMID: 31142515
- PMCID: PMC6724736
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0218
The Highly Recurrent PP2A Aα-Subunit Mutation P179R Alters Protein Structure and Impairs PP2A Enzyme Function to Promote Endometrial Tumorigenesis
Abstract
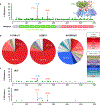
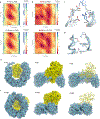
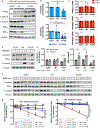
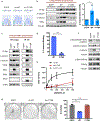
Somatic mutation of the protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) Aα-subunit gene PPP2R1A is highly prevalent in high-grade endometrial carcinoma. The structural, molecular, and biological basis by which the most recurrent endometrial carcinoma-specific mutation site P179 facilitates features of endometrial carcinoma malignancy has yet to be fully determined. Here, we used a series of structural, biochemical, and biological approaches to investigate the impact of the P179R missense mutation on PP2A function. Enhanced sampling molecular dynamics simulations showed that arginine-to-proline substitution at the P179 residue changes the protein's stable conformation profile. A crystal structure of the tumor-derived PP2A mutant revealed marked changes in A-subunit conformation. Binding to the PP2A catalytic subunit was significantly impaired, disrupting holoenzyme formation and enzymatic activity. Cancer cells were dependent on PP2A disruption for sustained tumorigenic potential, and restoration of wild-type Aα in a patient-derived P179R-mutant cell line restored enzyme function and significantly attenuated tumorigenesis and metastasis in vivo. Furthermore, small molecule-mediated therapeutic reactivation of PP2A significantly inhibited tumorigenicity in vivo. These outcomes implicate PP2A functional inactivation as a critical component of high-grade endometrial carcinoma disease pathogenesis. Moreover, they highlight PP2A reactivation as a potential therapeutic strategy for patients who harbor P179R PPP2R1A mutations. SIGNIFICANCE: This study characterizes a highly recurrent, disease-specific PP2A PPP2R1A mutation as a driver of endometrial carcinoma and a target for novel therapeutic development.See related commentary by Haines and Huang, p. 4009.
©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement:
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and Case Western Reserve University on behalf of the author G.N. have filed patents covering composition of matter on the small molecules disclosed herein for the treatment of human cancer and other diseases and for methods of use for using these small molecule PP2A activators. RAPPTA Therapeutics LLC has licensed this intellectual property for the clinical and commercial development of this series of small molecule PP2A activators. The author G.N. has an ownership interest in RAPPTA Therapeutics LLC.
Figures

Comment in
-
Precision Therapy for Aggressive Endometrial Cancer by Reactivation of Protein Phosphatase 2A.Cancer Res. 2019 Aug 15;79(16):4009-4010. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-1938. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31416848
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD & Jemal A Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin 68, 7–30 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Cantrell LA, Blank SV & Duska LR Uterine carcinosarcoma: A review of the literature. Gynecol Oncol 137, 581–588 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Arend R, Doneza JA & Wright JD Uterine carcinosarcoma. Curr Opin Oncol 23, 531–536 (2011). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F30 CA224979/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL068863/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR031845/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008803/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA240993/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 CA224977/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR002547/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007250/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA181654/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 TR002549/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL107147/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL130209/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL081064/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA138421/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA197780/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR018390/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL103453/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

