Role of the Srs2-Rad51 Interaction Domain in Crossover Control in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 31142613
- PMCID: PMC6707447
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.119.302337
Role of the Srs2-Rad51 Interaction Domain in Crossover Control in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
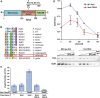
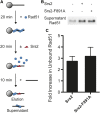
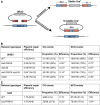
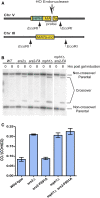
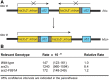
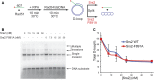
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Srs2, in addition to its well-documented antirecombination activity, has been proposed to play a role in promoting synthesis-dependent strand annealing (SDSA). Here we report the identification and characterization of an SRS2 mutant with a single amino acid substitution (srs2-F891A) that specifically affects the Srs2 pro-SDSA function. This residue is located within the Srs2-Rad51 interaction domain and embedded within a protein sequence resembling a BRC repeat motif. The srs2-F891A mutation leads to a complete loss of interaction with Rad51 as measured through yeast two-hybrid analysis and a partial loss of interaction as determined through protein pull-down assays with purified Srs2, Srs2-F891A, and Rad51 proteins. Even though previous work has shown that internal deletions of the Srs2-Rad51 interaction domain block Srs2 antirecombination activity in vitro, the Srs2-F891A mutant protein, despite its weakened interaction with Rad51, exhibits no measurable defect in antirecombination activity in vitro or in vivo Surprisingly, srs2-F891A shows a robust shift from noncrossover to crossover repair products in a plasmid-based gap repair assay, but not in an ectopic physical recombination assay. Our findings suggest that the Srs2 C-terminal Rad51 interaction domain is more complex than previously thought, containing multiple interaction sites with unique effects on Srs2 activity.
Keywords: DNA repair; crossover control; genome stability; helicase; protein interaction; recombination.
Copyright © 2019 by the Genetics Society of America.
Figures

References
-
- Aboussekhra A., Chanet R., Zgaga Z., Cassier Chauvat C., Heude M., et al. , 1989. RADH, a gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encoding a putative DNA helicase involved in DNA repair. Characteristics of radH mutants and sequence of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 17: 7211–7219. 10.1093/nar/17.18.7211 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aboussekhra A., Chanet R., Adjiri A., Fabre F., 1992. Semi-dominant suppressors of Srs2 helicase mutations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae map in the RAD51 gene, whose sequence predicts a protein with similarities to procaryotic RecA protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 12: 3224–3234. 10.1128/MCB.12.7.3224 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

