[Lysis at the dorsal vertebral bodies showing chronic contained rupture of an aneurysm: about a case]
- PMID: 31143337
- PMCID: PMC6522157
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2019.32.32.17851
[Lysis at the dorsal vertebral bodies showing chronic contained rupture of an aneurysm: about a case]
Abstract
Chronic contained ruptures of aneurysms are extremely rare. They can result from aneurysm rupture. Indeed, the most dreaded complication of aneurysm is its rupture, which is often fatal. However, haematoma can exceptionally occur after rupture, which is contained by the surrounding anatomical structures, stopping aneurysm from leaking. Unlike the classic rupture, there are no signs of hemorrhagic shock. They are replaced by moderate pain and, often, by atypical signs such as lysis of the dorsal vertebral bodies caused by the occurrence of an hematoma detected by imaging, as in our case. It's important to know this disorder because chronic rupture requires surgical management due to the risk of later rupture of the haematoma.
Les anévrismes chroniques rompus contenus représentent une entité extrêmement rare, qui peut faire suite à une rupture d'anévrisme. En effet, la complication la plus à craindre de l'anévrisme est la rupture, qui est souvent mortelle. Toutefois exceptionnellement, il se formera un hématome suite à la rupture, lequel sera contenu par les structures anatomiques avoisinantes; ce qui permettra en outre d'arrêter la fuite. Contrairement à la rupture classique, les signes de choc hémorragique seront absents; remplacés par une simple douleur modérée, et des signes souvent atypiques tels que la lyse du rachis dorsal par l'hématome constitué, découverte à l'imagerie dans notre cas. La connaissance de cette entité est importante, car la rupture chronique nécessite une prise en charge chirurgicale; du fait du risque de rupture ultérieure de l'hématome.
Keywords: Chronic contained rupture of an aneurysm; lysis; vertebral body.
Conflict of interest statement
Les auteurs ne déclarent aucun conflit d'intérêts.
Figures

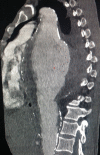
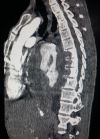

References
-
- Cronenwett JL, Murphy TF, Zelenock GB, Whitehouse WM, Jr, Lindenauer SM, Graham LM, Quint LE, Silver TM, Stanley JC. "Actuarial analysis of variables associated with rupture of small abdominal aortic aneurysms".Surgery. September. 1985;98(3):472–83. - PubMed
-
- Davies RR, Goldstein LJ, Coady MA, et al. « Yearly rupture or dissection rates for aortic aneurysms: simple prediction based on size ». Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;73(1):17–28. - PubMed
-
- Sraieb T, Ben Ameur Y, Bougamra S, Longo S, Ben Romdhane N, Manaa J, et al. "Chronic-contained ruptured aortic aneurysm: un unusual cause of back pain".Tunis Med. 2004; 82(11):1052–5. - PubMed
-
- Vinay Kumar, Abul Abbas K, Nelson Fausto, Richard Mitchell N. Robbins basic pathology. Eighth Edition(8th) Edition. Saunders/Elsevier; 2007.
-
- Booth M I, Galland R B. "Chronic contained rupture of an abdominal aortic aneurysm: a case report and review of the Literature". Ejves Extra. 2002;3:33–35.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
