Secondary Observer System for Detection of Microaneurysms in Fundus Images Using Texture Descriptors
- PMID: 31144148
- PMCID: PMC7064709
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-019-00225-z
Secondary Observer System for Detection of Microaneurysms in Fundus Images Using Texture Descriptors
Abstract
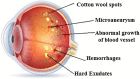
The increase of diabetic retinopathy patients and diabetic mellitus worldwide yields lot of challenges to ophthalmologists in the screening of diabetic retinopathy. Different signs of diabetic retinopathy were identified in retinal images taken through fundus photography. Among these stages, the early stage of diabetic retinopathy termed as microaneurysms plays a vital role in diabetic retinopathy patients. To assist the ophthalmologists, and to avoid vision loss among diabetic retinopathy patients, a computer-aided diagnosis is essential that can be used as a second opinion while screening diabetic retinopathy. On this vision, a new methodology is proposed to detect the microaneurysms and non-microaneurysms through the stages of image pre-processing, candidate extraction, feature extraction, and classification. The feature extractor, generalized rotational invariant local binary pattern, contributes in extracting the texture-based features of microaneurysms. As a result, our proposed system achieved a free-response receiver operating characteristic score of 0.421 with Retinopathy Online Challenge database.
Keywords: Diabetic retinopathy; Fundus image; Local binary pattern; Microaneurysms; Optic disc.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Microaneurysms detection in color fundus images using machine learning based on directional local contrast.Biomed Eng Online. 2020 Apr 15;19(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12938-020-00766-3. Biomed Eng Online. 2020. PMID: 32295576 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of microaneurysms using ant colony algorithm in the early diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy.Med Hypotheses. 2019 Aug;129:109242. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2019.109242. Epub 2019 May 21. Med Hypotheses. 2019. PMID: 31371092
-
Automatic detection of microaneurysms in retinal fundus images.Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2017 Jan;55:106-112. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2016.08.001. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2017. PMID: 27595214
-
Computer-aided diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy: a review.Comput Biol Med. 2013 Dec;43(12):2136-55. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2013.10.007. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Comput Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 24290931 Review.
-
A review on computer-aided recent developments for automatic detection of diabetic retinopathy.J Med Eng Technol. 2019 Feb;43(2):87-99. doi: 10.1080/03091902.2019.1576790. Epub 2019 Jun 14. J Med Eng Technol. 2019. PMID: 31198073 Review.
Cited by
-
Deep Learning Approach for Automatic Microaneurysms Detection.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 11;22(2):542. doi: 10.3390/s22020542. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35062506 Free PMC article.
-
Microaneurysms detection in color fundus images using machine learning based on directional local contrast.Biomed Eng Online. 2020 Apr 15;19(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12938-020-00766-3. Biomed Eng Online. 2020. PMID: 32295576 Free PMC article.
-
Localization and grading of NPDR lesions using ResNet-18-YOLOv8 model and informative features selection for DR classification based on transfer learning.Heliyon. 2024 May 9;10(10):e30954. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30954. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38779022 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ministry of Health Malaysia Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Team . Diabetes mellitus and complications-Module. Putrajaya: Ministry of Health Malaysia; 2012.
-
- Kohner EM, Aldington SJ, Stratton IM, Manley SE, Holman RR, Matthews DR. United Kingdom prospective diabetes study, “Diabetic Retinopathy at Diagnosis of Noninsulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus And associated risk factors”. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998;116:297–303. doi: 10.1001/archopht.116.3.297. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

