The effect of early Helicobacter pylori eradication on the healing of ESD-induced artificial ulcers: A retrospective study
- PMID: 31145312
- PMCID: PMC6708934
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015807
The effect of early Helicobacter pylori eradication on the healing of ESD-induced artificial ulcers: A retrospective study
Abstract
Background: The role of Helicobacter pylori eradication is still not clear in endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD)-induced artificial ulcer. This study investigates the therapeutic effects of H. pylori eradication on ESD-induced artificial ulcers.
Methods: Eighty-four patients with ESD-induced artificial ulcers were enrolled. H. pylori eradication success subgroup (Group A1) and H. pylori eradication failure subgroups (Group A2) received standard triple therapy orally for 7 days, followed by esomeprazole 20 mg bis in die (bid) orally for the remainder of the treatment period (4 weeks in total). The H. pylori positive (Group B1) and H. pylori negative subgroups (Group B2) received esomeprazole 20 mg bid orally for 4 weeks. Ulcer healing was evaluated by gastroscopy, and H. pylori was identified by a C13 breath test or an Hp-RUT 2 and 6 months after treatment.
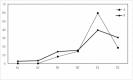
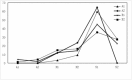
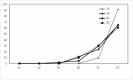
Results: Successful eradication of H. pylori can promote healing of ESD-induced artificial ulcers. The ESD-induced artificial ulcer healing rate in Group A1 was statistically higher than that in Groups A2, B1, and B2.
Conclusion: Our results indicated that early H. pylori eradication therapy can promote ESD-induced artificial ulcer healing in H. pylori positive patients with ESD-induced artificial ulcers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Sugano K. Detection and management of early gastric cancer. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol 2015;13:398–408. - PubMed
-
- Lim JH, Kim SG, Choi J, et al. Risk factors of delayed ulcer healing after gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection. Surg Endosc 2015;29:3666–73. - PubMed
-
- Higuchi K, Takeuchi T, Uedo N, et al. Efficacy and safety of 1-week Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy and 7-week rebamipide treatment after endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer in comparison with 8-week PPI standard treatment: a randomized, controlled, prospective, multicenter study. Gastric Cancer 2015;18:612–7. - PubMed
-
- Bornschein J, Rokkas T, Selgrad M, et al. Helicobacter pylori and clinical aspects of gastric cancer. Helicobacter 2009;14 suppl 1:41–5. - PubMed
-
- Kakushima N, Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, et al. Helicobacter pylori status and the extent of gastric atrophy do not affect ulcer healing after endoscopic submucosal dissection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;21:1586–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

