Classroom Standing Desks and Time-Series Variation in Sedentary Behavior and Physical Activity among Primary School Children
- PMID: 31146330
- PMCID: PMC6603736
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16111892
Classroom Standing Desks and Time-Series Variation in Sedentary Behavior and Physical Activity among Primary School Children
Abstract
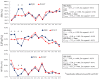
The purpose of the present study was to examine the effects of height-adjustable standing desks on time-series variation in sedentary behavior (SB) among primary school children. Thirty-eight children aged 11-12 years (22 boys and 16 girls) from two classes at a primary school in Nagano, Japan, participated in this study. One class was allocated as the intervention group and provided with individual standing desks for 6 months, and the other was allocated as the control group. Time spent in SB, light-intensity physical activity (LPA), and moderate-to-vigorous-intensity physical activity (MVPA) was measured using accelerometers (ActiGraph) at baseline and follow-up. Time spent in SB was significantly lower by 18.3 min/day on average in the intervention class at follow-up (interaction effects: F(1, 36) = 4.95, p = 0.035, η2 = 0.082). This was accompanied by a significant increase in time spent in MVPA (+19.9 min/day on average). Our time-series analysis showed significant decreases in SB during school time, while no change in SB was found during non-school time. This result indicates that the use of standing desks promotes an overall reduction in SB with no compensatory increase during non-school time.
Keywords: ActiGraph; health; height-adjustable desks; hourly variations; intervention; school-age children; sitting time.
Conflict of interest statement
The desks used in the present study were supplied via an in-kind donation from Okamura Co., Japan. The company played no role in the study design, analysis or in the preparation of this manuscript. There are no further competing interests to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Tremblay M.S., Aubert S., Barnes J.D., Saunders T.J., Carson V., Latimer-Cheung A.E., Chastin S.F.M., Altenburg T.M., Chinapaw M.J.M. Sedentary Behavior Research Network (SBRN)—Terminology Consensus Project process and outcome. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017;14:75. doi: 10.1186/s12966-017-0525-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tremblay M.S., LeBlanc A.G., Kho M.E., Saunders T.J., Larouche R., Colley R.C., Goldfield G., Connor Gorber S. Systematic review of sedentary behaviour and health indicators in school-aged children and youth. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011;8:98. doi: 10.1186/1479-5868-8-98. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carson V., Hunter S., Kuzik N., Gray C.E., Poitras V.J., Chaput J.P., Saunders T.J., Katzmarzyk P.T., Okely A.D., Connor Gorber S., et al. Systematic review of sedentary behaviour and health indicators in school-aged children and youth: An update. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016;41:S240–S265. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2015-0630. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

