MRSA: the leading pathogen of orthopedic infection in a tertiary care hospital, South India
- PMID: 31148966
- PMCID: PMC6531934
- DOI: 10.4314/ahs.v19i1.12
MRSA: the leading pathogen of orthopedic infection in a tertiary care hospital, South India
Abstract
Background: The rate of infection is high and heterogeneous in developing countries. This study aimed to find the rate and pattern of infection in a tertiary care hospital with a goal to improve the infection control practices.
Methods: The study was conducted in the orthopedic units of a multispecialty teaching hospital. Medical records of major orthopedic surgery adult patients without immunosuppression state were included. The bacterial culture report of the wound swabs were noted over a period of one year. The bacterial culture testing was performed by a recommended method.
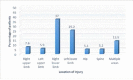
Results: Among 2,249 orthopedic surgery patients, 83.7% were males, 49.1% had open wounds during admission and 32.2% patients were infected. Majority (64.2%) of the injuries were in the lower limb with 19.4% patients having undergone multiple surgeries during hospitalization. A total of 946 pathogens were grown from 725 specimens. Staphylococcus aureus was the maximum (48.4%) followed by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (26.3%) and E coli (16.7%). Among them, 57.3% were Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and was the leading pathogen causing infection among orthopedic patients.
Conclusion: MRSA infection was high. Consequent to this, an interventional program entitled 'Extended Infection Control Measures' was designed to reduce the burden of infection.
Keywords: MRSA; South India; infection; orthopedic.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organisation, author. Health care-associated infections Fact sheet. World Heal Organisation; [cited 2016 November 22]. 2015;4. Available from: http://www.who.int/gpsc/country_work/gpsc_ccisc_fact_sheet_en.pdf.
-
- Hospital-acquired infections high in India. 2011. Sep 22, [cited 2017 January 21]. Avaialable from: http://www.indiamedicaltimes.com/2011/09/22/hospital-acquired-infections....
-
- Patted SM, Chinagudi S, Soragavi VR, Bhavi SB. The prevalence of MRSA infection in orthopaedic surgery in a Medical College Hospital : A 2-year analysis. Biomed Res-India. 2013;24(1):33–35.
-
- Dhawan B, Mohanty S, Das BK, Kapil A. Bacteriology of orthopaedic wound infections in an Indian Tertiary Care Hospital. Indian J Med Res. 2005 Apr;121:784–785. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal AC, Jain S, Jain RK, Raza HKT. Pathogenic bacteria in an orthopaedic hospital in India. J Infect Developing Countries. 2008;2(2):120–123. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical