SERUM NESFATIN-1 LEVEL IN HEALTHY SUBJECTS WITH WEIGHT-RELATED ABNORMALITIES AND NEWLY DIAGNOSED PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS; A CASE-CONTROL STUDY
- PMID: 31149062
- PMCID: PMC6535324
- DOI: 10.4183/aeb.2019.69
SERUM NESFATIN-1 LEVEL IN HEALTHY SUBJECTS WITH WEIGHT-RELATED ABNORMALITIES AND NEWLY DIAGNOSED PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS; A CASE-CONTROL STUDY
Abstract
Context: Nesfatin-1 is a novel peptide with both central and peripheral anorexigenic regulatory properties. Besides its effects on food intake, few studies have suggested a possible role for this peptide in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus type 2.
Objective: To compare serum levels of nesfatin-1 between healthy, normal-weight persons and three groups including healthy underweight, healthy obese and diabetic subjects.
Design: Prospective, case-control study, performed between January 2015 and January 2016.
Subjects and methods: Fasting levels in serum nesfatin-1 were measured in 30 healthy, normal-weight individuals (controls), 30 healthy underweight persons, 30 healthy obese persons, and 30 patients with newly diagnosed diabetes type 2 using standard enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits.
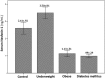
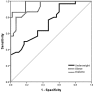
Results: The mean serum nesfatin-1 level was significantly higher in controls (2.61 ng/mL) compared to that in obese (1.13 ng/mL) and diabetic (0.99 ng/mL) patients; and significantly lower than that in the underweight group (3.50 ng/mL). The obese and diabetic groups were comparable in this regard. No significant association was found between serum nesfatin-1 level and age, sex, or body mass index.
Conclusions: Serum nesfatin-1 is possibly associated with weight-related abnormalities in otherwise healthy subjects and diabetes type 2. Obesity and diabetes type 2 may share a common pathologic point in this regard.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; nesfatin-1; obesity; underweight.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Oh IS, Shimizu H, Satoh T, Okada S, Adachi S, Inoue K, Eguchi H, Yamamoto M, Imaki T, Hashimoto K, Tsuchiya T, Monden T, Horiguchi K, Yamada M, Mori M. Identification of nesfatin-1 as a satiety molecule in the hypothalamus. Nature. 2006;443(7112):709–712. - PubMed
-
- Mohan H, Gasner M, Ramesh N, Unniappan S. Ghrelin, ghrelin-O-acyl transferase, nucleobindin-2/nesfatin-1 and prohormone convertases in the pancreatic islets of Sprague Dawley rats during development. J Mol Histol. 2016;47(3):325–336. - PubMed
-
- Nakata M, Gantulga D, Santoso P, Zhang B, Masuda C, Mori M, Okada T, Yada T. Paraventricular NUCB2/nesfatin-1 supports oxytocin and vasopressin neurons to control feeding behavior and fluid balance in male mice. Endocrinology. 2016;157(6):2322–2332. - PubMed
-
- Ozcan M, Gok ZB, Kacar E, Serhatlioglu I, Kelestimur H. Nesfatin-1 increases intracellular calcium concentration by protein kinase C activation in cultured rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neurosci Lett. 2016;619:177–181. - PubMed
-
- Prinz P, Goebel-Stengel M, Teuffel P, Rose M, Klapp BF, Stengel A. Peripheral and central localization of the nesfatin-1 receptor using autoradiography in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;470(3):521–527. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
