Catheter type, placement and insertion techniques for preventing catheter-related infections in chronic peritoneal dialysis patients
- PMID: 31149735
- PMCID: PMC6543877
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004680.pub3
Catheter type, placement and insertion techniques for preventing catheter-related infections in chronic peritoneal dialysis patients
Abstract
Background: Peritonitis is one of the limiting factors for the growth of peritoneal dialysis (PD) worldwide and is a major cause of technique failure. Several studies have examined the effectiveness of various catheter-related interventions for lowering the risk of PD-related peritonitis. This is an update of a review first published in 2004.
Objectives: To evaluate the role of different catheter implantation techniques and catheter types in lowering the risk of PD-related peritonitis in PD patients.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Kidney and Transplant Register of Studies up to 15 January 2019 through contact with the Information Specialist using search terms relevant to this review. Studies in the Register are identified through searches of CENTRAL, MEDLINE, and EMBASE, conference proceedings, the International Clinical Trials Register (ICTRP) Search Portal and ClinicalTrials.gov.
Selection criteria: Studies comparing different catheter insertion techniques, catheter types, use of immobilisation techniques and different break-in periods were included. Studies of different PD sets were excluded.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently assessed study quality and extracted data. Statistical analyses were performed using a random effects model and the results expressed as risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
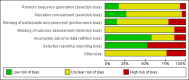
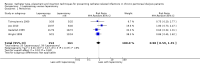
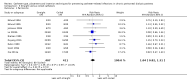
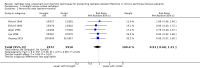
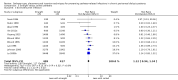
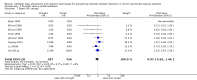
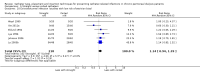
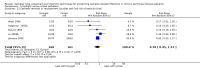
Main results: Forty-two studies (3144 participants) were included: 18 evaluated techniques of catheter implantation, 22 examined catheter types, one assessed an immobiliser device, and one examined break-in period. In general, study quality was variable and almost all aspects of study design did not fulfil CONSORT standards for reporting.Catheter insertion by laparoscopy compared with laparotomy probably makes little or no difference to the risks of peritonitis (RR 0.90, 95% CI 0.59 to 1.35; moderate certainty evidence), exit-site/tunnel infection (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.43 to 2.31; low certainty evidence), catheter removal/replacement (RR 1.20, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.86; low certainty evidence), technique failure (RR 0.71, 95% CI 0.47 to 1.08; low certainty evidence), and death (all causes) (RR 1.26, 95% CI 0.72 to 2.20; moderate certainty evidence). It is uncertain whether subcutaneous burying of catheter increases peritonitis (RR 1.16, 95% CI 0.37 to 3.60; very low certainty evidence). Midline insertion compared to lateral insertion probably makes little or no difference to the risks of peritonitis (RR 0.65, 95% CI 0.32 to 1.33; moderate certainty evidence) and may make little or no difference to exit-site/tunnel infection (RR 0.56, 95% CI 0.12 to 2.58; low certainty evidence). Percutaneous insertion compared with open surgery probably makes little or no difference to the exit-site/tunnel infection (RR 0.16, 95% CI 0.02 to 1.30; moderate certainty evidence).Straight catheters probably make little or no difference to the risk of peritonitis (RR 1.04, 95% CI 0.82 to 1.31; moderate certainty evidence), peritonitis rate (RR 0.91, 95% CI 0.68 to 1.21; moderate certainty evidence), risk of exit-site infection (RR 1.12, 95% CI 0.94 to 1.34; moderate certainty evidence), and exit-site infection rate (RR 1.05, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.43; moderate certainty evidence) compared to coiled catheter. It is uncertain whether straight catheters prevent catheter removal or replacement (RR 1.11, 95% CI 0.73 to 1.66; very low certainty evidence) but straight catheters probably make little or no difference to technique failure (RR 0.82, 95% CI 0.51 to 1.31; moderate certainty evidence) and death (all causes) (RR 0.95, 95% CI 0.62 to 1.46; low certainty evidence) compared to coiled catheter. Tenckhoff catheter with artificial curve at subcutaneous tract compared with swan-neck catheter may make little or no difference to peritonitis (RR 1.29, 95% CI 0.85 to 1.96; low certainty evidence) and incidence of exit-site/tunnel infection (RR 0.96, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.21; low certainty evidence) but may slightly improve exit-site infection rate (RR 0.67, 95% CI 0.50 to 0.90; low certainty evidence).
Authors' conclusions: There is no strong evidence that any catheter-related intervention, including the use of different catheter types or different insertion techniques, reduces the risks of PD peritonitis or other PD-related infections, technique failure or death (all causes). However, the numbers and sizes of studies were generally small and the methodological quality of available studies was suboptimal, such that the possibility that a particular catheter-related intervention might have a beneficial effect cannot be completely ruled out with confidence.
Conflict of interest statement
Professor David Johnson is a current recipient of a National Health and Medical Research Council Practitioner Fellowship. Professor David Johnson has received consultancy fees, research grants, speaker’s honoraria and travel sponsorships for Baxter Healthcare and Fresenius Medical Care. He has also received a consulting fee from AstraZeneca and travel grants from Amgen
Yeoungjee Cho is a current recipient of a National Health and Medical Research Council Early Career Fellowship and has in the past received research grants from Fresenius Medical Care.
Figures


































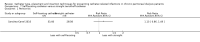



















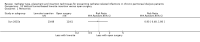













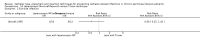


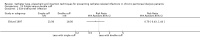






















Update of
-
Catheter type, placement and insertion techniques for preventing peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004 Oct 18;(4):CD004680. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004680.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 May 31;5:CD004680. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004680.pub3. PMID: 15495125 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Akcicek 1995 {published data only}
-
- Akcicek F, Ok E, Tokut Y, Cirit M, Kursal A, Unsul A, et al. Comparison the effect of laparoscopic Moncrief‐Popovich technique (LMPT) and blind Trocar technique (BTT) on early CAPD complications [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 1995;10(6):1037. [CENTRAL: CN‐00261138]
Akyol 1990 {published data only}
-
- Akyol AM, Porteous C, Brown MW. A comparison of two types of catheters for continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). Peritoneal Dialysis International 1990;10(1):63‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Al‐Hwiesh 2016 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Hwiesh A, Nasreldin M. The Saudi peritoneal dialysis catheter: Modified catheter and new technique: farewell to catheter migration [abstract no: SP456]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2016;31(Suppl 1):i244. [EMBASE: 72326558]
-
- Al‐Hwiesh AK. A modified peritoneal dialysis catheter with a new technique: farewell to catheter migration. Saudi Journal of Kidney Diseases & Transplantation 2016;27(2):281‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Atapour 2011 {published data only}
-
- Atapour A, Asadabadi HR, Karimi S, Eslami A, Beigi AA. Comparing the outcomes of open surgical procedure and percutaneously peritoneal dialysis catheter (PDC) insertion using laparoscopic needle: a two month follow‐up study. Journal of Research in Medical Sciences 2011;16(4):463‐8. [EMBASE: 2011292097] - PMC - PubMed
Buijsen 1994 {published data only}
-
- Buijsen JGM, Kox C, Boeschoten EW, Struijk DG. Randomized trial to compare single cuff (Sc) with double cuff (Dc) straight tenckhoff catheter (Tc) in CAPD patients (pt) [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 1994;9(5):583. [CENTRAL: CN‐00444579]
-
- Struijk DG, Kox C, vd Heijden‐Buijsen JG. Randomized trial of single cuff (sc) versus double cuff (dc) peritoneal dialysis catheter [abstract]. 35th Congress. European Renal Association. European Dialysis and Transplantation Association; 1998 Jun 6‐9; Rimini, Italy. 1998:315. [CENTRAL: CN‐00486056]
Chen 2014a {published data only}
-
- Chen G, Liu H, Zhou L, Wang P, Peng Y, Liu FU. Greater omentum folding in open surgical placement of PD catheters: a randomized controlled study and systemic review [abstract no: FR‐PO965]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2013;24:582A. - PubMed
-
- Chen G, Wang P, Liu H, Zhou L, Cheng M, Liu Y, et al. Greater omentum folding in the open surgical placement of peritoneal dialysis catheters: a randomized controlled study and systemic review. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2014;29(3):687‐97. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Danielsson 2002 {published data only}
-
- Danielsson A, Blohme L, Tranaeus A, Hylander B. A prospective randomized study of the effect of a subcutaneously "buried" peritoneal dialysis catheter technique versus standard technique on the incidence of peritonitis and exit‐site infection. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2002;22(2):211‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Danielsson A, Blohme L, Tranaeus A, Hylander B. Prospective randomized study of the impact a subcutaneous rest‐peroid of a PD‐catheter has on the incidence of peritonitis [abstract no: A0832]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1997;8(Program & Abstracts):178A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00444979]
Dasgupta 1998 {published data only}
-
- Dasgupta MK, Fox S, Card J, Maitland C, Perry D. Catheter survival is improved by the use of Moncrief‐Popovich catheters [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1998;9(Program & Abstracts):190A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00444987]
Ejlersen 1990 {published data only}
-
- Ejlersen E, Steven K, Lokkergaard H. Paramedian versus midline incision for the insertion of permanent peritoneal dialysis catheters. A randomized clinical trial. Scandinavian Journal of Urology & Nephrology 1990;24(2):151‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Eklund 1994 {published data only}
-
- Eklund BH, Honkanen EO, Kala AR, Kyllonen LE. Catheter configuration and outcome in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis: a prospective comparison of two catheters. Peritoneal Dialysis International 1994;14(1):70‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Eklund 1995 {published data only}
-
- Eklund BH, Honkanen EO, Kala AR, Kyllonen LE. Peritoneal dialysis access: prospective randomized comparison of the Swan neck and Tenckhoff catheters. Peritoneal Dialysis International 1995;15(8):353‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Eklund 1997 {published data only}
-
- Eklund B, Honkanen E, Kyllonen L, Salmela K, Kala AR. Peritoneal dialysis access: prospective randomized comparison of single‐cuff and double‐cuff straight Tenckhoff catheters. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 1997;12(2):2664‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gadallah 1999 {published data only}
-
- Gadallah MF, Pervez A, El‐Shahawy M, Sorrells D, Zibari G, McDonald J, et al. Peritoneoscopic versus surgical placement of Tenckhoff catheters: a prospective study on outcome [abstract no: A0904]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1996;7(9):1428. [CENTRAL: CN‐01658199] - PubMed
-
- Gadallah MF, Pervez A, el‐Shahawy MA, Sorrells D, Zibari G, McDonald J, et al. Peritoneoscopic versus surgical placement of peritoneal dialysis catheters: a prospective randomized study on outcome. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1999;33(1):118‐22. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Johnson 2006 {published data only}
-
- Johnson DW, Wong J, Wiggins KJ, Kirwan R, Griffin A, Preston J, et al. A randomized controlled trial of coiled versus straight swan‐neck Tenckhoff catheters in peritoneal dialysis patients. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2006;48(5):812‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Wong JS, Wiggins KJ, Campbell SB, Isbel NM, Mudge DW, Hawley CM, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of coiled versus straight swan neck tenckhoff catheters in peritoneal dialysis patients [abstract no: 1550]. Nephrology 2006;11(Suppl 2):A16. - PubMed
Jwo 2010 {published data only}
-
- Jwo SC, Chen KS, Lee CC, Chen HY. Prospective randomized study for comparison of open surgery with laparoscopic‐assisted placement of Tenckhoff peritoneal dialysis catheter‐‐a single center experience and literature review. Journal of Surgical Research 2010;159(1):489‐96. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Li 2009e {published data only}
-
- Li CL, Cui TG, Gan HB, Cheung K, Lio WI, Kuok UI. A randomized trial comparing conventional swan‐neck straight‐tip catheters to straight‐tip catheters with an artificial subcutaneous swan neck. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2009;29(3):278‐84. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lo 2003b {published data only}
-
- Lo WK, Lui SL, Li FK, Choy BY, Lam MF, Tse KC, et al. A prospective randomized study on three different peritoneal dialysis catheters. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2003;23 Suppl 2:S127‐31. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lye 1996 {published data only}
-
- Lye WC, Kour NW, Straaten JC, Leong SO, Lee EJ. A prospective randomized comparison of the Swan neck, coiled, and straight Tenckhoff catheters in patients on CAPD. Peritoneal Dialysis International 1996;16 Suppl 1:S333‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Merrikhi 2014 {published data only}
-
- Merrikhi A, Beigi AA, Raji Asadabadi H, Gheisari A, Karimi SH. The outcomes of percutaneously peritoneal dialysis catheter placement in comparison with open surgical method in children [abstract no: P177]. Iranian Journal of Kidney Diseases 2011;5(Suppl 1):37. [EMBASE: 70539682]
-
- Merrikhi A, Raji Asadabadi H, Beigi AA, Marashi SM, Ghaheri H, Nasiri Zarch Z. Comparison of percutaneous versus open surgical techniques for placement of peritoneal dialysis catheter in children: a randomized clinical trial. Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran 2014;28:38. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Moncrief 1998 {published data only}
-
- Moncrief JW, Popovich PP. Subcutaneous buried versus standard peritoneal dialysis catheter [abstract]. XVIII Annual CAPD Conference; 1998 Feb 24; Nashville (TN). 1998. [CENTRAL: CN‐00776340]
Nielsen 1995 {published data only}
-
- Nielsen PK, Hemmingsen C, Friis SU, Ladefoged J, Olgaard K. Comparison of straight and curled Tenckhoff peritoneal dialysis catheters implanted by percutaneous technique: a prospective randomized study. Peritoneal Dialysis International 1995;15(1):18‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ouyang 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ouyang CJ, Huang FX, Yang QQ, Jiang ZP, Chen W, Qiu Y, et al. Comparing the incidence of catheter‐related complications with straight and coiled tenckhoff catheters in peritoneal dialysis patients‐a single‐center prospective randomized trial. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2015;35(4):443‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Park 1998 {published data only}
-
- Park MS, Yim AS, Chung SH, Lee EY, Cha MK, Kim JH, et al. Effect of prolonged subcutaneous implantation of peritoneal catheter on peritonitis rate during CAPD: a prospective randomized study. Blood Purification 1998;16(3):171‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Qian 2014 {published data only}
-
- Qian X, Qi J. Preliminary report: cystoscopy‐assisted peritoneal dialysis catheter placement ‐ a direct, visual, safe, precise, easy, minimally invasive, and inexpensive technique. Clinical Nephrology 2014;81(4):247‐50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rubin 1990 {published data only}
-
- Rubin J, Didlake R, Raju S, Hsu H. A prospective randomized evaluation of chronic peritoneal catheters. Insertion site and intraperitoneal segment. ASAIO Transactions 1990;36(3):M497‐500. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sanchez‐Canel 2016 {published data only}
Scott 1994 {published data only}
-
- Scott PD, Bakran A, Pearson R, Riad H, Parrott N, Johnson RW, et al. Peritoneal dialysis access. Prospective randomized trial of 3 different peritoneal catheters‐‐preliminary report. Peritoneal Dialysis International 1994;14(3):289‐90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
SIPROCE 1997 {published data only}
-
- Pommer W. The efficiency of a silver ring to prevent exit‐site and other catheter‐related infections in PD‐patients‐final results of the SIPROCE study [abstract no: A0849]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1997;8(Program & Abstracts):182A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00447255]
-
- Pommer W, Brauner M, Westphale HJ, Brunkhorst R, Kramer R, Bundschu D, et al. Effect of a silver device in preventing catheter‐related infections in peritoneal dialysis patients: silver ring prophylaxis at the catheter exit study. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1998;32(5):752‐60. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- SIPROCE Study Group. Efficiency of a silver ring in preventing exit‐site infections in adult PD patients: results of the SIPROCE Study. Silver ring Prophylaxis of the Catheter Exit Site. Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis 1997;13:227‐32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Stegmayr 2005a {published data only}
-
- Stegmayr BG, Wikdahl AM, Bergström M, Nilsson C, Engman U, Arnerlöv C, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing the function of straight and coiled Tenckhoff catheters for peritoneal dialysis. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2005;25(1):85–8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Stegmayr 2015 {published data only}
Sun 2015a {published data only}
-
- Sun C, Zhang M, Jiang C. Vertical tunnel‐based low‐site peritoneal dialysis catheter implantation decreases the incidence of catheter malfunction. American Surgeon 2015;81(11):1157‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Timely PD 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ranganathan D, John GT, Yeoh E, Williams N, O'Loughlin B, Han T, et al. A randomized controlled trial to determine the appropriate time to initiate peritoneal dialysis after insertion of catheter (Timely PD Study). Peritoneal Dialysis International 2017;37(4):420‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Trooskin 1990 {published data only}
-
- Trooskin SZ, Harvey RA, Lennard TW, Greco RS. Failure of demonstrated clinical efficacy of antibiotic‐bonded continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) catheters. Peritoneal Dialysis International 1990;10(1):57‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tsimoyiannis 2000 {published data only}
-
- Tsimoyiannis EC, Siakas P, Glantzounis G, Toli C, Sferopoulos G, Pappas M, et al. Laparoscopic placement of the Tenckhoff catheter for peritoneal dialysis. Surgical Laparoscopy, Endoscopy & Percutaneous Techniques 2000;10(4):218‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Turner 1992 {published data only}
-
- Turner K, Edgar D, Hair M, Uttley L, Sternland R, Hunt L, et al. Does catheter immobilization reduce exit‐site infections in CAPD patients?. Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis 1992;8:265‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Voss 2012 {published data only}
-
- Voss D. Prospective randomised trial of radiological and surgical tenckhoff catheter insertion [abstract no: 101]. Nephrology 2004;9(Suppl 1):A26. [CENTRAL: CN‐00509548]
-
- Voss D, Hawkins S, Poole G, Marshall M. Radiological versus surgical implantation of first catheter for peritoneal dialysis: a randomized non‐inferiority trial. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2012;27(11):4196–204. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Winch 2000 {published data only}
-
- Winch P, Saltissi D, McGiffin C, Nathanson L, O'Loughlin B. Comparison between swan‐neck (SN) and straight curled (SC) double‐cuff catheters on peritoneal dialysis (PD) catheter‐related complications [abstract no: 29]. Nephrology 2000;5(1‐2 Suppl):A10. [CENTRAL: CN‐01657505]
Wright 1999 {published data only}
-
- Sellars L, Bel'eed K, Stoves J, Eadington D, Johnson B, Wright M, et al. Randomized trial of conventional vs laparoscopically assisted peritoneal catheter insertion techniques (interim report) [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1997;8(Program & Abstracts):182A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00447669]
-
- Wright MJ, Bel'eed K, Johnson BF, Eadington DW, Sellars L, Farr MJ. Randomized prospective comparison of laparoscopic and open peritoneal dialysis catheter insertion. Peritoneal Dialysis International 1999;19(4):372‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Xie 2011a {published data only}
-
- Xie J, Kiryluk K, Ren H, Zhu P, Huang X, Shen P, et al. Coiled versus straight peritoneal dialysis catheters: a randomized controlled trial and meta‐analysis. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2011;58(6):946‐55. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Yip 2010 {published data only}
-
- Yip T, Lui SL, Tse KC, Xu H, Ng FS, Cheng SW, et al. A prospective randomized study comparing Tenckhoff catheters inserted using the triple incision method with standard swan neck catheters. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2010;30(1):56‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zhang 2016 {published data only}
-
- Zhang Q, Jiang C, Zhu W, Sun C, Xia Y, Tang T, et al. Peritoneal catheter fixation combined with straight upward tunnel and low implant position to prevent catheter malfunction. Nephrology 2016;23(3):247‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zhu 2015 {published data only}
-
- Zhu W, Jiang C, Zheng X, Zhang M, Guo H, Yan X. The placement of peritoneal dialysis catheters: a prospective randomized comparison of open surgery versus "Mini‐Perc" technique. International Urology & Nephrology 2015;47(2):377‐82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Crabtree 2003 {published data only}
-
- Crabtree JH, Burchette RJ, Siddiqi RA, Huen IT, Hadnott LL, Fishman A. The efficacy of silver‐ion implanted catheters in reducing peritoneal dialysis‐related infections. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2003;23(4):368‐74. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
ISRCTN87054124 {published data only}
-
- Sudhindran S. Prospective randomised trial of laparoscopic versus closed insertion of tenckhoff catheters for peritoneal dialysis access. www.controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN87054124 (first received 12 September 2003).
Moncrief 1994 {published data only}
-
- Moncrief JW, Popovich RP. Moncrief‐Popovich catheter: implantation technique and clinical results. Peritoneal Dialysis International 1994;14 Suppl 3:S56‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
N0547061060 {published data only}
-
- Rhodes M. Prospective randomised trial of laparoscopic sutured versus blind (conventional) insertion of tenckhoff peritoneal dialysis catheters. www.nihr.ac.uk/Profile/Pages/NRRResults.aspx?publication_id=N0547061060 (last accessed July 2004).
O'Dwyer 2005 {published data only}
-
- O'Dwyer H, Fotheringham T, O'Kelly P, Doyle S, Haslam P, McGrath F, et al. A prospective comparison of two types of tunneled hemodialysis catheters: the Ash Split versus the PermCath. Cardiovascular & Interventional Radiology 2005;28(1):23‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Williams 1989 {published data only}
-
- Williams AJ, Boletis I, Johnson BF, Raftery AT, Cohen GL, Moorhead PJ, et al. Tenckhoff catheter replacement or intraperitoneal urokinase: a randomised trial in the management of recurrent continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) peritonitis. Peritoneal Dialysis International 1989;9(1):65‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Ahmad 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ahmad SF, Liu WJ, Mohd Y, Kandasami ND, Hooi LS, Gunn KB. Randomized controlled trial of peritoneoscopic vs open surgical placement of peritoneal dialysis catheters [abstract]. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2010;30(Suppl 2):S95. [EMBASE: 71928045]
LOCI 2011 {published data only}
-
- Lafranca JA, Hagen SM, Akkersdijk GP, Wever JJ, Kimenai HJ, Wabbijn M, et al. Laparoscopic vs open peritoneal dialysis catheter insertion, the LOCI‐trial [abstract]. European Surgical Research 2014;52(3‐4):139. [EMBASE: 71493264]
Wong 2004b {published data only}
-
- Wong FS, Chau S, Chow N, Ho JC, Cheng Y, Yu AW. Effect of changing transfer set on relapse of bacterial peritonitis. Hong Kong Journal of Nephrology 2004;6(2):87‐91. [EMBASE: 2004491078]
References to ongoing studies
NCT01023191 {published data only}
-
- Chetter IC. Open versus percutaneous insertion of CAPD catheters. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01023191 (date first received 2 December 2009).
NCT02479295 {published data only}
-
- Chow KM. Straight versus coiled peritoneal dialysis catheter for peritoneal dialysis patients. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02479295 (date first received 24 June 2015).
Additional references
Barraclough 2010
-
- Barraclough K, Hawley CM, McDonald SP, Brown FG, Rosman JB, Wiggins KJ, et al. Polymicrobial peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis patients in Australia: predictors, treatment, and outcomes. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2010;55(1):121‐31. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Boudville 2012
Campbell 2016
Chow 2005
-
- Chow KM, Szeto CC, Leung CB, Kwan BC, Law MC, Li PK. A risk analysis of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis‐related peritonitis. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2005;25(4):374–9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
CONSORT 2001
-
- Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman DG. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel‐group randomised trials. Lancet 2001;357(9263):1191‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Edey 2010
-
- Edey M, Hawley CM, McDonald SP, Brown FG, Rosman JB, Wiggins KJ, et al. Enterococcal peritonitis in Australian peritoneal dialysis patients: predictors, treatment and outcomes in 116 cases. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2010;25(4):1272‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Egger 1997
GRADE 2008
GRADE 2011
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction‐GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):383‐94. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hagen 2014
-
- Hagen SM, Lafranca JA, Ijzermans JN, Dor FJ. A systematic review and meta‐analysis of the influence of peritoneal dialysis catheter type on complication rate and catheter survival. Kidney International 2014;85(4):920–32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Htay 2017
-
- Htay H, Cho Y, Pascoe EM, Darssan D, Nadeau‐Fredette AC, Hawley C, et al. Multicenter registry analysis of center characteristics associated with technique failure in patients on incident peritoneal dialysis. Clinical Journal of The American Society of Nephrology: CJASN 2017;12(7):1090‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Htay 2018
-
- Htay H, Cho Y, Pascoe EM, Darssan D, Nadeau‐Fredette AC, Hawley C, et al. Center effects and peritoneal dialysis peritonitis outcomes: analysis of a national registry. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2018;74(6):814‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jegatheesan 2018
-
- Jegatheesan D, Johnson DW, Cho Y, Pascoe EM, Darssan D, Htay H, et al. The relationship between body mass index and organism‐specific peritonitis. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2018;38(3):206‐14. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kolesnyk 2010
-
- Kolesnyk I, Dekker FW, Boeschoten EW, Krediet RT. Time‐dependent reasons for peritoneal dialysis technique failure and mortality. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2010;30(2):170‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kotsanas 2007
-
- Kotsanas D, Polkinghorne KR, Korman TM, Atkins RC, Brown F. Risk factors for peritoneal dialysis‐related peritonitis: can we reduce the incidence and improve patient selection?. Nephrology 2007;12(3):239–45. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Li 2016
Li 2017
-
- Li PK, Chow KM, Luijtgaarden MW, Johnson DW, Jager KJ, Mehrotra R, et al. Changes in the worldwide epidemiology of peritoneal dialysis. Nature Reviews Nephrology 2017;13(2):90‐103. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lim 2011
-
- Lim WH, Boudville N, McDonald SP, Gorham G, Johnson DW, Jose M. Remote indigenous peritoneal dialysis patients have higher risk of peritonitis, technique failure, all‐cause and peritonitis‐related mortality. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2011;26(10):3366–72. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lindblad 1988
-
- Lindblad AS, Hamilton RW, Nolph KD, Novak JW. A retrospective analysis of catheter configuration and cuff type: a National CAPD Registry report. Peritoneal Dialysis International 1988;8(2):129–33. [EMBASE: 18252569]
McDonald 2004
-
- McDonald SP, Collins JF, Rumpsfeld M, Johnson DW. Obesity is a risk factor for peritonitis in the Australian and New Zealand peritoneal dialysis patient populations. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2004;24(4):340–6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mehrotra 2016
Ong 2016
-
- Ong LM, Ch'ng CC, Wee HC, Supramaniam P, Zainal H, Goh BL, et al. Risk of peritoneal dialysis‐related peritonitis in a multi‐racial Asian population. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2017;37(1):35‐43. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Piraino 2002
-
- Piraino B. Peritonitis as a complication of peritoneal dialysis. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2002;9(10):1956‐64. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schaefer 2003
-
- Schaefer F. Management of peritonitis in children receiving chronic peritoneal dialysis. Paediatric Drugs 2003;5(5):315‐25. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schünemann 2011a
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and 'Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Schünemann 2011b
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Shen 2013
Spence 1985
-
- Spence PA, Mathews RE, Khanna R, Oreopoulos DG. Improved results with a paramedian technique for the insertion of peritoneal dialysis catheters. Surgery, Gynecology & Obstetrics 1985;161(6):585‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Strippoli 2004a
Szeto 2017
-
- Szeto CC, Li PK, Johnson DW, Bernardini J, Dong J, Figueiredo AE, et al. ISPD catheter‐related infection recommendations: 2017 update. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2017;37(2):141‐54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wu 2013
Xu 2009
-
- Xu G, Tu W, Xu C. Mupirocin for preventing exit‐site infection and peritonitis in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2010;25(2):587–92. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Strippoli 2003
Strippoli 2004
Strippoli 2004b
-
- Strippoli GF, Tong A, Johnson D, Schena FP, Craig JC. Catheter‐related interventions to prevent peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis: a systematic review of randomized, controlled trials. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2004;15(10):2735‐46. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

