Hostile attribution bias and angry rumination: A longitudinal study of undergraduate students
- PMID: 31150488
- PMCID: PMC6544285
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217759
Hostile attribution bias and angry rumination: A longitudinal study of undergraduate students
Abstract
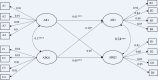
Angry rumination and hostile attribution bias are important cognitive factors of aggression. Although prior theoretical models of aggression suggest that aggressive cognitive factors may influence each other, there are no studies examining the longitudinal relationship between angry rumination and hostile attribution bias. The present study used cross-lagged structural equation modeling to explore the longitudinal mutual relationship between hostile attribution bias and angry rumination; 941 undergraduate students (38.5% male) completed questionnaires assessing the variables at two time points. The results indicate that hostile attribution bias showed a small but statistically significant effect on angry rumination 6 months later, and angry rumination showed a quite small but marginally significant effect on hostile attribution bias across time. The present study supports the idea that hostile attribution bias influences angry rumination, and argue that the relationship between angry rumination and hostile attribution bias may be mutual. Additionally, the results suggest that there may be a causal relation of different aggression-related cognitive factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Longitudinal relations between bullying victimization and aggression: The multiple mediation effects of anger rumination and hostile automatic thoughts.Psych J. 2024 Oct;13(5):849-859. doi: 10.1002/pchj.760. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Psych J. 2024. PMID: 38655612 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between trait anger and reactive aggressive behavior in middle school students: the mediating role and intervention of hostile attribution bias.BMC Psychol. 2024 Aug 2;12(1):422. doi: 10.1186/s40359-024-01918-z. BMC Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39095875 Free PMC article.
-
Hostile Attribution Bias Mediates the Relationship Between Structural Variations in the Left Middle Frontal Gyrus and Trait Angry Rumination.Front Psychol. 2018 Apr 11;9:526. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00526. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2018. PMID: 29695990 Free PMC article.
-
The multiple systems model of angry rumination.Pers Soc Psychol Rev. 2013 May;17(2):103-23. doi: 10.1177/1088868312467086. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Pers Soc Psychol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23175519 Review.
-
The anatomy of anger: an integrative cognitive model of trait anger and reactive aggression.J Pers. 2010 Feb;78(1):9-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6494.2009.00607.x. J Pers. 2010. PMID: 20433611 Review.
Cited by
-
Rumination Mediates the Relation of Hostile Attribution to Psychological Maladjustment Among Adolescents from Three Countries.Res Child Adolesc Psychopathol. 2025 Jun;53(6):861-876. doi: 10.1007/s10802-025-01288-z. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Res Child Adolesc Psychopathol. 2025. PMID: 39888487 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of patients' hostile attribution bias on aggression in doctor-patient interactions.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 2;10(1):e23971. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e23971. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38268606 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal relations between bullying victimization and aggression: The multiple mediation effects of anger rumination and hostile automatic thoughts.Psych J. 2024 Oct;13(5):849-859. doi: 10.1002/pchj.760. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Psych J. 2024. PMID: 38655612 Free PMC article.
-
The role of anger rumination as a mediator in the relationship between driver moral disengagement and driving angry.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 5;10(8):e29112. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29112. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38644810 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal associations between cybervictimization, anger rumination, and cyberaggression.Aggress Behav. 2021 May;47(3):332-342. doi: 10.1002/ab.21958. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Aggress Behav. 2021. PMID: 33655507 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peled M, Moretti MM. Ruminating on rumination: Are rumination on anger and sadness differentially related to aggression and depressed mood? Journal of Psychopathology & Behavioral Assessment. 2010;32(1):108–117. 10.1007/s10862-009-9136-2 - DOI
-
- Denson TF, Pedersen WC, Friese M, Hahm A, Roberts L. Understanding impulsive aggression: Angry rumination and reduced self-control capacity are mechanisms underlying the provocation-aggression relationship. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin. 2011;37(6):850–862. 10.1177/0146167211401420 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

