CD4 count recovery and associated factors among individuals enrolled in the South African antiretroviral therapy programme: An analysis of national laboratory based data
- PMID: 31150489
- PMCID: PMC6544279
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217742
CD4 count recovery and associated factors among individuals enrolled in the South African antiretroviral therapy programme: An analysis of national laboratory based data
Abstract
Background: We describe CD4 count recovery among HIV positive individuals who initiated antiretroviral therapy (ART) with and without severe immune suppression using complete laboratory data from South Africa's national HIV treatment programme between 2010 and 2014 and discuss implications for CD4 count monitoring.
Methods: Retrospective analysis of routinely collected laboratory data from South Africa's National Health Laboratory Service (NHLS). A probabilistic record linkage algorithm was used to create a cohort of HIV positive individuals who initiated ART between 2010 and 2014 based on timing of CD4 count and viral load measurements. A CD4 count < 50 copies/μl at ART initiation was considered severe immunosuppression. A multivariable piecewise mixed-effects linear regression model adjusting for age, gender, year of starting ART, viral suppression in follow up and province was used to predict CD4 counts during follow up.
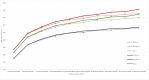
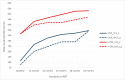
Results: 1,070,900 individuals had evidence of starting ART during 2010-2014 and met the criteria for inclusion in the cohort -46.6% starting ART with CD4 < 200 cells/μl and 10.1% with CD4 < 50 cells/ μl. For individuals with CD4 counts < 200 cells/μl, predicted CD4 counts > 200 cells/μl, >350 cells/μl and >500 cells/μl corresponded with mean follow up durations of 1.5 years (standard deviation [s.d] 1.1), 1.9years (s.d 1.2) and 2.1 years (s.d 1.3 years). For those with CD4 counts < 50 cells/μl, predicted CD4 count above these threshold corresponded with mean follow up durations of 2.5 years (s.d 0.9 years), 4.4 years (s.d 0.4 years) and 5.0 years (s.d 0.1years) for recovery to the same thresholds. CD4 count recovery varied mostly with duration on ART, CD4 count at the start of ART and gender.
Conclusion: For individuals starting with ART with severe immunosuppression, CD4 recovery to 200cells/μl did not occur or took longer than 12 month for significant proportions. CD4 monitoring and interventions recommended for advanced HIV disease should continue until full recovery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Factors Related to CD4+ T-Cell Recovery and Viral Suppression in Patients Who Have Low CD4+ T Cell Counts at the Initiation of HAART: A Retrospective Study of the National HIV Treatment Sub-Database of Zhejiang Province, China, 2014.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 22;11(2):e0148915. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148915. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26900702 Free PMC article.
-
Suboptimal immune recovery during antiretroviral therapy with sustained HIV suppression in sub-Saharan Africa.AIDS. 2018 May 15;32(8):1043-1051. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001801. AIDS. 2018. PMID: 29547445
-
Immune recovery in HIV-1 infected patients with sustained viral suppression under long-term antiretroviral therapy in Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 22;15(10):e0240880. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240880. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33091053 Free PMC article.
-
The future role of CD4 cell count for monitoring antiretroviral therapy.Lancet Infect Dis. 2015 Feb;15(2):241-7. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70896-5. Epub 2014 Nov 19. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25467647 Review.
-
The evolving role of CD4 cell counts in HIV care.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2017 Mar;12(2):123-128. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000348. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2017. PMID: 28059957 Review.
Cited by
-
Growth and CD4 patterns of adolescents living with perinatally acquired HIV worldwide, a CIPHER cohort collaboration analysis.J Int AIDS Soc. 2022 Mar;25(3):e25871. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25871. J Int AIDS Soc. 2022. PMID: 35255197 Free PMC article.
-
A Multistate Continuous Time-Inhomogeneous Markov Model for Assessing the CD4 Count Dynamics of HIV/AIDS Patients Undergoing Antiretroviral Therapy in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025 May 29;22(6):848. doi: 10.3390/ijerph22060848. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40566275 Free PMC article.
-
Combining CD4 count, CD8 count and CD4/CD8 ratio to predict risk of mortality among HIV-positive adults after therapy: a group-based multi-trajectory analysis.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 6;14:1269650. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1269650. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38124745 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent advanced HIV disease in rural KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa: Trends, characteristics, and the urgent need for targeted interventions.PLoS One. 2025 Feb 18;20(2):e0317674. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0317674. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39965033 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring HIV infection in Minas Gerais state: 15-year assessment of adults living with HIV initiating Antiretroviral Therapy.Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2020 Dec 11;53:e20200360. doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0360-2020. eCollection 2020. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2020. PMID: 33331608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaufmann GR, Bloch M, Zaunders JJ, Smith D, Cooper DA (2000) Long-term immunological response in HIV-1-infected subjects receiving potent antiretroviral therapy. Aids 14: 959–969. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous