Exercise upregulates copeptin levels which is not regulated by interleukin-1
- PMID: 31150497
- PMCID: PMC6544286
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217800
Exercise upregulates copeptin levels which is not regulated by interleukin-1
Abstract
Objective: Studies have suggested that arginine vasopressin (AVP) and its surrogate marker copeptin increase during exercise, independently of serum sodium and/or osmolality. In extreme cases, this can lead to runners-induced hyponatremia. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) increases during exercise and induces AVP in animal models. We here therefore investigate whether copeptin (a surrogate marker for AVP) increases upon exercise in young and healthy males, and whether this increase is regulated by IL-1.
Design: In a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, crossover trial in 17 healthy male volunteers, the effect of the IL-1 receptor antagonist anakinra on exercise-induced copeptin was compared with placebo.
Methods: Participants exercised for one hour at 75% of VO2max and were not allowed to drink/eat 6 hours before and during the study. Participants received either 100 mg of anakinra or placebo 1h before exercise. Blood was drawn at certain time intervals.
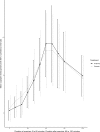
Results: In both groups, copeptin levels were induced by 2.5-fold upon exercise (p<0.001), from 4.5-10.6 pmol/l in the placebo, and 4.3-11.3 pmol/l in the anakinra group, (p = 0.38). One hour after exercise, copeptin levels dropped to 7.7 and 7.9 pmol/l in the placebo and anakinra group, respectively (p = 0.58). The increase of copeptin levels was not explained by sodium concentrations.
Conclusions: Exercise induces a continuous rise of plasma copeptin levels in healthy male volunteers independently of sodium levels and fluid intake. This increase is not regulated by the IL-1 pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous