Leptin-induced Trafficking of KATP Channels: A Mechanism to Regulate Pancreatic β-cell Excitability and Insulin Secretion
- PMID: 31151172
- PMCID: PMC6600549
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20112660
Leptin-induced Trafficking of KATP Channels: A Mechanism to Regulate Pancreatic β-cell Excitability and Insulin Secretion
Abstract
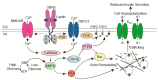
The adipocyte hormone leptin was first recognized for its actions in the central nervous system to regulate energy homeostasis but has since been shown to have direct actions on peripheral tissues. In pancreatic β-cells leptin suppresses insulin secretion by increasing KATP channel conductance, which causes membrane hyperpolarization and renders β-cells electrically silent. However, the mechanism by which leptin increases KATP channel conductance had remained unresolved for many years following the initial observation. Recent studies have revealed that leptin increases surface abundance of KATP channels by promoting channel trafficking to the β-cell membrane. Thus, KATP channel trafficking regulation has emerged as a mechanism by which leptin increases KATP channel conductance to regulate β-cell electrical activity and insulin secretion. This review will discuss the leptin signaling pathway that underlies KATP channel trafficking regulation in β-cells.
Keywords: ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channel; Insulin secretion; Leptin; β-cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

