Development of the Inhibitors that Target the PD-1/PD-L1 Interaction-A Brief Look at Progress on Small Molecules, Peptides and Macrocycles
- PMID: 31151293
- PMCID: PMC6600339
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24112071
Development of the Inhibitors that Target the PD-1/PD-L1 Interaction-A Brief Look at Progress on Small Molecules, Peptides and Macrocycles
Abstract
Cancer immunotherapy based on antibodies targeting the immune checkpoint PD-1/PD-L1 pathway has seen unprecedented clinical responses and constitutes the new paradigm in cancer therapy. The antibody-based immunotherapies have several limitations such as high production cost of the antibodies or their long half-life. Small-molecule inhibitors of the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction have been highly anticipated as a promising alternative or complementary therapeutic to the monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). Currently, the field of developing anti-PD-1/PD-L1 small-molecule inhibitors is intensively explored. In this paper, we review anti-PD-1/PD-L1 small-molecule and peptide-based inhibitors and discuss recent structural and preclinical/clinical aspects of their development. Discovery of the therapeutics based on small-molecule inhibitors of the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction represents a promising but challenging perspective in cancer treatment.
Keywords: PD-1/PD-L1 pathway; cancer immunotherapy; cocrystal structures; lead optimization; peptide-based and small synthetic molecule inhibitors; rational drug design; scaffold hopping; structure-activity relationship.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


















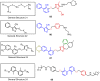

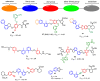
Similar articles
-
Discovery of low-molecular weight anti-PD-L1 peptides for cancer immunotherapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Oct 22;7(1):270. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0705-y. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31640814 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in PD-1/PD-L1 pathway inhibitors: From biomacromolecules to small molecules.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Jan 15;186:111876. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111876. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31761384 Review.
-
Development of Inhibitors of the Programmed Cell Death-1/Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Signaling Pathway.J Med Chem. 2019 Feb 28;62(4):1715-1730. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00990. Epub 2018 Oct 9. J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30247903 Review.
-
Insights into non-peptide small-molecule inhibitors of the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction: Development and perspective.Bioorg Med Chem. 2021 Mar 1;33:116038. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2021.116038. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Bioorg Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33517226 Review.
-
Immunomodulators targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 protein-protein interaction: From antibodies to small molecules.Med Res Rev. 2019 Jan;39(1):265-301. doi: 10.1002/med.21530. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Med Res Rev. 2019. PMID: 30215856 Review.
Cited by
-
Tryptophan: A Rheostat of Cancer Immune Escape Mediated by Immunosuppressive Enzymes IDO1 and TDO.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 23;12:636081. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636081. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33708223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Competition NMR for Detection of Hit/Lead Inhibitors of Protein-Protein Interactions.Molecules. 2020 Jul 1;25(13):3017. doi: 10.3390/molecules25133017. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32630327 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical potential of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade therapy for renal cell carcinoma (RCC): a rapidly evolving strategy.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Dec 12;22(1):401. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02816-3. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 36510217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 2-Hydroxy-4-phenylthiophene-3-carbonitrile as PD-L1 Antagonist and Its Comparison to Available Small Molecular PD-L1 Inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2023 Jul 27;66(14):9577-9591. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00254. Epub 2023 Jul 14. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37450644 Free PMC article.
-
CCX559 is a potent, orally-administered small molecule PD-L1 inhibitor that induces anti-tumor immunity.PLoS One. 2023 Jun 7;18(6):e0286724. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286724. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37285333 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

