HPV Epitope Processing Differences Correlate with ERAP1 Allotype and Extent of CD8+ T-cell Tumor Infiltration in OPSCC
- PMID: 31151965
- PMCID: PMC6640044
- DOI: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0498
HPV Epitope Processing Differences Correlate with ERAP1 Allotype and Extent of CD8+ T-cell Tumor Infiltration in OPSCC
Abstract
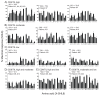
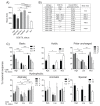
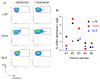
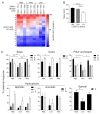
Presence of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) predicts survival in many cancer types. In HPV-driven cancers, cervical and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas (CSCC and OPSCC, respectively), numbers of infiltrating T cells, particularly CD8+ T cells, and presentation of HPV E6/E7 epitopes are associated with improved prognosis. Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (ERAP1) regulates the presented peptide repertoire, trimming peptide precursors prior to MHC I loading. ERAP1 is polymorphic, and allotypic variation of ERAP1 enzyme activity has an impact on the presented peptide repertoire. Individual SNPs are associated with incidence and outcome in a number of diseases, including CSCC. Here, we highlight the requirement for ERAP1 in the generation of HPV E6/E7 epitopes and show that the functional activity of ERAP1 allotype combinations identified in OPSCC correlate with tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T-cell (CD8)/TIL (CD8/TIL) status of the tumor. Functional analyses revealed that ERAP1 allotype combinations associated with CD8/TILlow tumors have a reduced capacity to generate both a model antigen SIINFEHL and the HPV-16 E782-90 epitope LLMGTLGIV from N-terminally extended precursor peptides. In contrast, ERAP1 allotypes from CD8/TILhigh tumors generated the epitopes efficiently. These data reveal that ERAP1 function correlates with CD8/TIL numbers and, by implication, prognosis, suggesting that the presentation of HPV-16 epitopes at the cell surface, resulting in an anti-HPV T-cell response, may depend on the ERAP1 allotype combinations expressed within an individual.
©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tumor-infiltrating B cells affect the progression of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma via cell-to-cell interactions with CD8+ T cells.J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Oct 17;7(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0726-6. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31623665 Free PMC article.
-
ERAP1 allotypes shape the epitope repertoire of virus-specific CD8+ T cell responses in acute hepatitis C virus infection.J Hepatol. 2019 Jun;70(6):1072-1081. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.01.034. Epub 2019 Feb 13. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30769005 Free PMC article.
-
ERAP1-Dependent Antigen Cross-Presentation Determines Efficacy of Adoptive T-cell Therapy in Mice.Cancer Res. 2018 Jun 15;78(12):3243-3254. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1946. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29559473
-
Immune cells and prognosis in HPV-associated oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas: Review of the literature.Oral Oncol. 2016 Jul;58:8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2016.04.004. Epub 2016 May 7. Oral Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27311396 Review.
-
Shedding new light on the role of ERAP1 in Type 1 diabetes: A perspective on disease management.Autoimmun Rev. 2023 Apr;22(4):103291. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2023.103291. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Autoimmun Rev. 2023. PMID: 36740089 Review.
Cited by
-
Common allotypes of ER aminopeptidase 1 have substrate-dependent and highly variable enzymatic properties.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100443. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100443. Epub 2021 Feb 20. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33617882 Free PMC article.
-
New novel non-MHC genes were identified for cervical cancer with an integrative analysis approach of transcriptome-wide association study.J Cancer. 2021 Jan 1;12(3):840-848. doi: 10.7150/jca.47918. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33403041 Free PMC article.
-
ERAP Inhibitors in Autoimmunity and Immuno-Oncology: Medicinal Chemistry Insights.J Med Chem. 2024 Jul 25;67(14):11597-11621. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00840. Epub 2024 Jul 16. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39011823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymorphic positions 349 and 725 of the autoimmunity-protective allotype 10 of ER aminopeptidase 1 are key in determining its unique enzymatic properties.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 18;15:1415964. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1415964. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39493758 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview on ERAP Roles in Infectious Diseases.Cells. 2020 Mar 14;9(3):720. doi: 10.3390/cells9030720. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32183384 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Galon J, Costes A, Sanchez-Cabo F, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Lagorce-Pages C, Tosolini M, Camus M, Berger A, Wind P, Zinzindohoue F, et al. Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science. 2006;313:1960–1964. - PubMed
-
- Leffers N, Gooden MJ, de Jong RA, Hoogeboom BN, ten Hoor KA, Hollema H, Boezen HM, van der Zee AG, Daemen T, Nijman HW. Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating T-lymphocytes in primary and metastatic lesions of advanced stage ovarian cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009;58:449–459. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Noble F, Mellows T, McCormick Matthews LH, Bateman AC, Harris S, Underwood TJ, Byrne JP, Bailey IS, Sharland DM, Kelly JJ, Primrose JN, et al. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes correlate with improved survival in patients with oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2016;65:651–662. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Piersma SJ, Jordanova ES, van Poelgeest MI, Kwappenberg KM, van der Hulst JM, Drijfhout JW, Melief CJ, Kenter GG, Fleuren GJ, Offringa R, van der Burg SH. High number of intraepithelial CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is associated with the absence of lymph node metastases in patients with large early-stage cervical cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67:354–361. - PubMed
-
- Welters MJP, Ma W, Santegoets S, Goedemans R, Ehsan I, Jordanova ES, van Ham VJ, van Unen V, Koning F, van Egmond SI, Charoentong P, et al. Intratumoral HPV16-Specific T Cells Constitute a Type I-Oriented Tumor Microenvironment to Improve Survival in HPV16-Driven Oropharyngeal Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:634–647. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

