SOX2 is required for inner ear growth and cochlear nonsensory formation before sensory development
- PMID: 31152002
- PMCID: PMC6633603
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.170522
SOX2 is required for inner ear growth and cochlear nonsensory formation before sensory development
Abstract
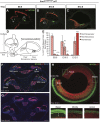
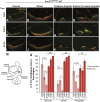
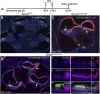
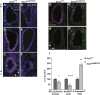
The transcription factor sex determining region Y-box 2 (SOX2) is required for the formation of hair cells and supporting cells in the inner ear and is a widely used sensory marker. Paradoxically, we demonstrate via fate mapping that, initially, SOX2 primarily marks nonsensory progenitors in the mouse cochlea, and is not specific to all sensory regions until late otic vesicle stages. SOX2 fate mapping reveals an apical-to-basal gradient of SOX2 expression in the sensory region of the cochlea, reflecting the pattern of cell cycle exit. To understand SOX2 function, we undertook a timed-deletion approach, revealing that early loss of SOX2 severely impaired morphological development of the ear, whereas later deletions resulted in sensory disruptions. During otocyst stages, SOX2 shifted dramatically from a lateral to medial domain over 24-48 h, reflecting the nonsensory-to-sensory switch observed by fate mapping. Early loss or gain of SOX2 function led to changes in otic epithelial volume and progenitor proliferation, impacting growth and morphological development of the ear. Our study demonstrates a novel role for SOX2 in early otic morphological development, and provides insights into the temporal and spatial patterns of sensory specification in the inner ear.
Keywords: Cochlea; Inner ear; Mouse; Otocyst; SOX2; Sensory; Specification.
© 2019. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Figures






References
-
- Amador-Arjona A., Cimadamore F., Huang C. T., Wright R., Lewis S., Gage F. H. and Terskikh A. V. (2015). SOX2 primes the epigenetic landscape in neural precursors enabling proper gene activation during hippocampal neurogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112, E1936-E1945. 10.1073/pnas.1421480112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

