Another piece of the puzzle added to understand t(4;11) leukemia better
- PMID: 31152087
- PMCID: PMC6545855
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2018.213397
Another piece of the puzzle added to understand t(4;11) leukemia better
Figures
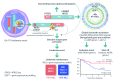
Comment on
-
Unraveling the cellular origin and clinical prognostic markers of infant B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia using genome-wide analysis.Haematologica. 2019 Jun;104(6):1176-1188. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.206375. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Haematologica. 2019. PMID: 30679323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trentin L, Giordan M, Dingermann T, et al. Two independent gene signatures in pediatric t(4;11) acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. Eur J Haematol. 2009;83(5):406–419. - PubMed
-
- Stam RW, Schneider P, Hagelstein JA, et al. Gene expression profiling-based dissection of MLL translocated and MLL germline acute lymphoblastic leukemia in infants. Blood. 2010;115(14):2835–2844. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

