Down-regulation of microRNA-138 improves immunologic function via negatively targeting p53 by regulating liver macrophage in mice with acute liver failure
- PMID: 31152110
- PMCID: PMC6639459
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20190763
Down-regulation of microRNA-138 improves immunologic function via negatively targeting p53 by regulating liver macrophage in mice with acute liver failure
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Down-regulation of microRNA-138 improves immunologic function via negatively targeting p53 by regulating liver macrophage in mice with acute liver failure.Biosci Rep. 2023 Jun 28;43(6):BSR-2019-0763_RET. doi: 10.1042/BSR-2019-0763_RET. Biosci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37317591 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
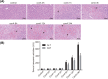
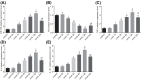
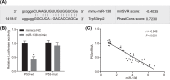
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been frequently identified as key mediators in almost all developmental and pathological processes, including those in the liver. The present study was conducted with aims of investigating the role of microRNA-138 (miR-138) in acute liver failure (ALF) via a mechanism involving p53 and liver macrophage in a mouse model. The ALF mouse model was established using C57BL/6 male mice via tail vein injection of Concanamycin A (Con A) solution. The relationship between miR-138 and p53 was tested. The mononuclear macrophages were infected with mimic and inhibitor of miR-138 in order to identify roles of miR-138 in p53 and levels of inflammatory factors. Reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), Western blot analysis and ELISA were conducted in order to determine the levels of miR-138, inflammatory factors, and p53 during ALF. The results showed an increase in the levels of miR-138 and inflammatory factors in ALF mice induced by the ConA as time progressed and reached the peak at 12 h following treatment with ConA, while it was on the contrary when it came to the level of p53. Dual-luciferase reporter gene assay revealed that p53 was a target gene of miR-138. Furthermore, the results from the in vitro transfection experiments in primary macrophages of ALF mouse showed that miR-138 down-regulated p53 and enhanced levels of inflammatory factors; thus, improving immune function in ALF mice. In conclusion, by negatively targeting p53, the decreased miR-138 improves immunologic function by regulating liver macrophage in mouse models of ALF.
Keywords: Acute liver failure; Immune function; Macrophage; P53; microRNA-138.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

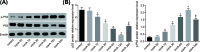


References
-
- Siveen K.S., Nguyen A.H., Lee J.H., Li F., Singh S.S., Kumar A.P.. et al. (2014) Negative regulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 signalling cascade by lupeol inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Br. J. Cancer 111, 1327–133710.1038/bjc.2014.422 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

