Diagnostic values and appropriate cutoff points of lipid ratios in patients with abnormal glucose tolerance status: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 31153374
- PMCID: PMC6545201
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-019-1070-z
Diagnostic values and appropriate cutoff points of lipid ratios in patients with abnormal glucose tolerance status: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Lipid ratios, for example total cholesterol/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TC/HDL-C) and triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C), are associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, the predictive values of lipid ratios in prediabetes remain unclear. The aims of this study were: 1) to investigate the association between lipid ratios and abnormal glucose tolerance; 2) to compare the predictive significance of lipid ratios with commonly used indicators of lipid variables in clinical practice in a Chinese population.
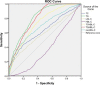
Methods: The cross-sectional study enrolled 2680 participants from the Health Promotion Center of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University. All participants received a 75 g oral glucose tolerance test. Blood samples were obtained at baseline and 120 min after glucose ingestion. Participants were classified as normal glucose tolerance (NGT), impaired glucose regulation (IGR), and T2DM. The odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were estimated using logistic regression model. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to identify the cutoff points of lipid and lipid ratios. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), sensitivity and specificity were calculated to estimate their diagnostic values.
Results: TC, TG, TC/HDL-C, TG/HDL-C and non-HDL-C were significantly correlated with both prediabetes and T2DM after adjustment for other risk factors such as blood glucose, whereas LDL-C was only positively correlated with prediabetes. TG and TG/HDL-C showed higher diagnostic values for prediabetes and T2DM than TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, TC/HDL-C and non-HDL-C, with the AUC values over 0.70. For predicting prediabetes, the optimal cutoff point was 1.36 mmol/l for TG and 1.13 for TG/HDL-C. For predicting T2DM, the optimal cutoff point was 1.46 mmol/l for TG and 1.22 for TG/HDL-C.
Conclusions: Both TG and TG/HDL-C are promising biomarkers for distinguishing individuals with abnormal glucose tolerance, and can be used to predict prediabetes and T2DM in Chinese population.
Keywords: Diabetes; Dyslipidemia; Glucose tolerance; Lipid ratio.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Xu Y, Wang L, He J, Bi Y, Li M, Wang T, Wang L, Jiang Y, Dai M, Lu J, Xu M, Li Y, Hu N, Li J, Mi S, Chen C, Li G, Mu Y, Zhao J, Kong L, Chen J, Lai S, Wang W, Zhao W, Ning G. Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA. 2013;310(9):948–959. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.168118. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

