Apolipoprotein E polymorphisms contribute to statin response in Chinese ASCVD patients with dyslipidemia
- PMID: 31153375
- PMCID: PMC6545221
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-019-1069-5
Apolipoprotein E polymorphisms contribute to statin response in Chinese ASCVD patients with dyslipidemia
Abstract
Background: Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) plays an important role in lipid metabolism and clearance. Statins are the most common drugs used to modulate the lipid profile in the clinic therapy; the associations between ApoE polymorphisms and statin response to lipids were inconsistent in previous studies among different ethnicities. Our study aimed to demonstrate the relationships among the statins response and the ApoE gene common polymorphisms and lifestyle risk factors in Chinese arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) patients with dyslipidemia.
Methods: A total of 1002 dyslipidemia ASCVD patients were recruited in this study, including 311 patients with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). These patients were all treated with drugs atorvastatin (10 mg/d) or rosuvastatin (5 mg/d) for at least 4 weeks and genotyped for ApoE e2/e3/e4 alleles, using Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP) and Sanger sequencing. The plasma lipids levels were determined before and after statins treatment.
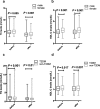
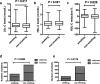
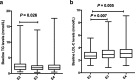
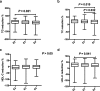
Results: The results of ApoE genotyping with KASP method were consistent with the sequencing analysis. In the total 1002 patients, the E2 phenotypes (e2/e3, e2/e2) had significant lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) baseline levels than subjects with E3 (e3/e3, e2/e4) and E4 (e3/e4, e4/e4) phenotypes (P = 0.007, 0.005, respectively), and E2 phenotypes had the highest triglyceride (TG) baseline levels. To statins treatment, E2 phenotypes had a better response in TG, Total cholesterol (TC) and LDL-C reduction percentage compared with other phenotypes, and smoking/alcohol drinking status also had a significant influence on statins response of LDL-C lowering. No significant difference was found in the effects of lipids decreasing between atorvastatin and rosuvastatin drugs in all patients.
Conclusions: We developed the KASP technique for the ApoE genotyping, and demonstrated ApoE polymorphisms interacted with smoking/drinking to influence the declining extent of TG, TC and LDL-C levels after statins therapy in Chinese dyslipidemia ASCVD patients. These discoveries developed our cognition with the genetic polymorphisms effects on statin response, which should be taken more seriously in smoking/drinking E4 amino acid isoform carriers.
Keywords: Apolipoprotein E; KASP; Polymorphism; Statins response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Lahoz C, Peña R, Mostaza JM, et al. Baseline levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and lipoprotein (a) and the AvaII polymorphism of the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene influence the response of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol to pravastatin treatment. Metabolism. 2005;54(6):741–747. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2004.12.020. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

