Lactate Is a Natural Suppressor of RLR Signaling by Targeting MAVS
- PMID: 31155231
- PMCID: PMC6625351
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.003
Lactate Is a Natural Suppressor of RLR Signaling by Targeting MAVS
Abstract
RLR-mediated type I IFN production plays a pivotal role in elevating host immunity for viral clearance and cancer immune surveillance. Here, we report that glycolysis, which is inactivated during RLR activation, serves as a barrier to impede type I IFN production upon RLR activation. RLR-triggered MAVS-RIG-I recognition hijacks hexokinase binding to MAVS, leading to the impairment of hexokinase mitochondria localization and activation. Lactate serves as a key metabolite responsible for glycolysis-mediated RLR signaling inhibition by directly binding to MAVS transmembrane (TM) domain and preventing MAVS aggregation. Notably, lactate restoration reverses increased IFN production caused by lactate deficiency. Using pharmacological and genetic approaches, we show that lactate reduction by lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) inactivation heightens type I IFN production to protect mice from viral infection. Our study establishes a critical role of glycolysis-derived lactate in limiting RLR signaling and identifies MAVS as a direct sensor of lactate, which functions to connect energy metabolism and innate immunity.
Keywords: MAVS; RLR signaling; glucose metabolism; interferon; lactate.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
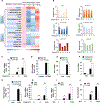

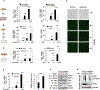
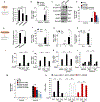
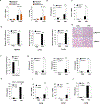
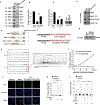
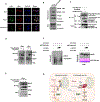
Comment in
-
Glucose Metabolism Linked to Antiviral Responses.Cell. 2019 Jun 27;178(1):10-11. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.057. Cell. 2019. PMID: 31251910
-
Antagonism between Antiviral Signaling and Glycolysis.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Sep;30(9):571-573. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2019.07.010. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31349923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker JC, Yan X, Peng T, Kasten S, and Roche TE (2000). Marked differences between two isoforms of human pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase. J Biol Chem 275, 15773–15781. - PubMed
-
- Brand A, Singer K, Koehl GE, Kolitzus M, Schoenhammer G, Thiel A, Matos C, Bruss C, Klobuch S, Peter K, et al. (2016). LDHA-Associated Lactic Acid Production Blunts Tumor Immunosurveillance by T and NK Cells. Cell Metab 24, 657–671. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Han C, Xie B, Hu X, Yu Q, Shi L, Wang Q, Li D, Wang J, Zheng P, et al. (2013a). Induction of Siglec-G by RNA viruses inhibits the innate immune response by promoting RIG-I degradation. Cell 152, 467–478. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

