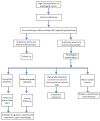
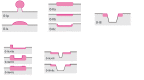
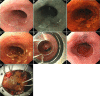
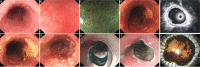
Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of esophageal carcinoma 2018 (English version)
- PMID: 31156297
- PMCID: PMC6513746
- DOI: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2019.02.01
Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of esophageal carcinoma 2018 (English version)
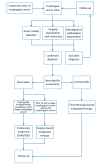
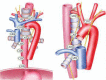
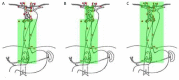
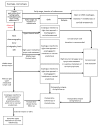
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
