Progesterone Actions During Central Nervous System Development
- PMID: 31156378
- PMCID: PMC6533804
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00503
Progesterone Actions During Central Nervous System Development
Abstract
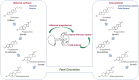
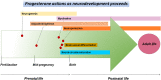
Although progesterone is a steroid hormone mainly associated with female reproductive functions, such as uterine receptivity and maintenance of pregnancy, accumulating data have shown its physiological actions to extend to several non-reproductive functions in the central nervous system (CNS) both in males and females. In fact, progesterone is de novo synthesized in specific brain regions by neurons and glial cells and is involved in the regulation of various molecular and cellular processes underlying myelination, neuroprotection, neuromodulation, learning and memory, and mood. Furthermore, progesterone has been reported to be implicated in critical developmental events, such as cell differentiation and neural circuits formation. This view is supported by the increase in progesterone synthesis observed during pregnancy in both the placenta and the fetal brain. In the present review, we will focus on progesterone actions during CNS development.
Keywords: brain sex differentiation; brain tumors; myelination; neurodevelopment; neuroprotection; progesterone; progesterone receptor.
Figures

References
-
- Bali N., Arimoto J. M., Iwata N., Lin S. W., Zhao L., Brinton R. D., et al. (2012). Differential responses of progesterone receptor membrane component-1 (Pgrmc1) and the classical progesterone receptor (Pgr) to 17β-estradiol and progesterone in hippocampal subregions that support synaptic remodeling and neurogenesis. Endocrinology 153 759–769. 10.1210/en.2011-1699 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

