Clinical Trials Required to Assess Potential Benefits and Side Effects of Treatment of Patients With Anorexia Nervosa With Recombinant Human Leptin
- PMID: 31156489
- PMCID: PMC6533856
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00769
Clinical Trials Required to Assess Potential Benefits and Side Effects of Treatment of Patients With Anorexia Nervosa With Recombinant Human Leptin
Abstract
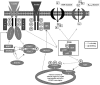
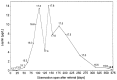
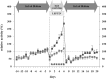
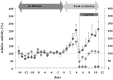
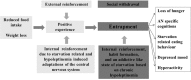
The core phenotype of anorexia nervosa (AN) comprises the age and stage dependent intertwining of both its primary and secondary (i.e., starvation induced) somatic and mental symptoms. Hypoleptinemia acts as a key trigger for the adaptation to starvation by affecting diverse brain regions including the reward system and by induction of alterations of the hypothalamus-pituitary-"target-organ" axes, e.g., resulting in amenorrhea as a characteristic symptom of AN. Particularly, the rat model activity-based anorexia (ABA) convincingly demonstrates the pivotal role of hypoleptinemia in the development of starvation-induced hyperactivity. STAT3 signaling in dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) plays a crucial role in the transmission of the leptin signal in ABA. In patients with AN, an inverted U-shaped relationship has been observed between their serum leptin levels and physical activity. Albeit obese and therewith of a very different phenotype, humans diagnosed with rare congenital leptin deficiency have starvation like symptoms including hypothalamic amenorrhea in females. Over the past 20 years, such patients have been successfully treated with recombinant human (rh) leptin (metreleptin) within a compassionate use program. The extreme hunger of these patients subsides within hours upon initiation of treatment; substantial weight loss and menarche in females ensue after medium term treatment. In contrast, metreleptin had little effect in patients with multifactorial obesity. Small clinical trials have been conducted for hypothalamic amenorrhea and to increase bone mineral density, in which metreleptin proved beneficial. Up to now, metreleptin has not yet been used to treat patients with AN. Metreleptin has been approved by the FDA under strict regulations solely for the treatment of generalized lipodystrophy. The recent approval by the EMA may offer, for the first time, the possibility to treat extremely hyperactive patients with AN off-label. Furthermore, a potential dissection of hypoleptinemia-induced AN symptoms from the primary cognitions and behaviors of these patients could ensue. Accordingly, the aim of this article is to review the current state of the art of leptin in relation to AN to provide the theoretical basis for the initiation of clinical trials for treatment of this eating disorder.
Keywords: anorexia; hyperactivity; leptin; metreleptin treatment; physical activity; starvation.
Figures

References
-
- Ahima R. S., Flier J. S. (2000a). Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 11 327–332. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

