The Challenges and Promise of Complement Therapeutics for Ocular Diseases
- PMID: 31156618
- PMCID: PMC6529562
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01007
The Challenges and Promise of Complement Therapeutics for Ocular Diseases
Abstract
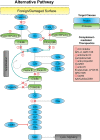
Ocular inflammation is a defining feature of sight threating diseases and its dysregulation can catalyze and or propagate ocular neurodegenerative maladies such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD). The complement system, an intrinsic component of the innate immunity, has an integral role in maintaining immune-surveillance and homeostasis in the ocular microenvironment; however, overstimulation can drive ocular inflammatory diseases. The mechanism for complement disease propagation in AMD is not fully understood, although there is accumulating evidence showing that targeted modulation of complement-specific proteins has the potential to become a viable therapeutic approach. To date, a major focus of complement therapeutics has been on targeting the alternative complement system in AMD. Recent studies have outlined potential complement cascade inhibitors that might mitigate AMD disease progression. First-in-class complement inhibitors target the modulation of complement proteins C3, C5, factor B, factor D, and properdin. Herein, we will summarize ocular inflammation in the context of AMD disease progression, current clinical outcomes and complications of complement-mediated therapeutics. Given the need for additional therapeutic approaches for ocular inflammatory diseases, targeted complement modulation has emerged as a leading candidate for eliminating inflammation-driven ocular maladies.
Keywords: age-related macular degeneration; complement system; immune modulation; ocular inflammation; therapeutics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complement System and Potential Therapeutics in Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 25;22(13):6851. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136851. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34202223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lutein and Factor D: two intriguing players in the field of age-related macular degeneration.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015 Apr 15;572:49-53. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2015.01.019. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 25637656 Review.
-
Targeting complement components C3 and C5 for the retina: Key concepts and lingering questions.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021 Jul;83:100936. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100936. Epub 2020 Dec 13. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 33321207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of complement inactivation by glycoprotein C of herpes simplex virus.J Immunol. 1997 Feb 15;158(4):1763-71. J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9029114
-
Activation of the alternative complement pathway.CRC Crit Rev Immunol. 1979 Nov;1(1):1-32. CRC Crit Rev Immunol. 1979. PMID: 162484 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Age-related macular degeneration and myeloproliferative neoplasms - A common pathway.Acta Ophthalmol. 2022 Oct;100 Suppl 271(Suppl 271):3-35. doi: 10.1111/aos.15247. Acta Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 36200281 Free PMC article.
-
Dimethyl Fumarate Blocks Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha-Driven Inflammation and Metabolic Rewiring in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Jun 23;15:896786. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.896786. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35813071 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances of exosomes in age-related macular degeneration.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 2;14:1204351. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1204351. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37332352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of dietary inflammatory index with ocular diseases: a population-based cross-sectional study.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jan 31;30(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02294-z. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 39891276 Free PMC article.
-
Murine Factor H Co-Produced in Yeast With Protein Disulfide Isomerase Ameliorated C3 Dysregulation in Factor H-Deficient Mice.Front Immunol. 2021 May 12;12:681098. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.681098. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34054871 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous