Modified Transosseous Wiring Technique for Neglected Fracture-Dislocation of the Proximal Interphalangeal Joint
- PMID: 31156775
- PMCID: PMC6526134
- DOI: 10.4055/cios.2019.11.2.220
Modified Transosseous Wiring Technique for Neglected Fracture-Dislocation of the Proximal Interphalangeal Joint
Abstract
Background: Fracture-dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint of the finger is challenging due to the high risk of stiffness. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the clinical and radiological results of a modified transosseous wiring technique for the management of chronic fracture-dislocations of the PIP joint.
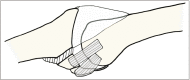
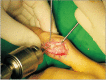
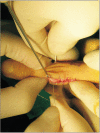
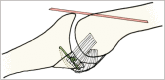
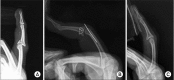
Methods: Ten patients (nine men and one woman; mean age, 38.3 years; range, 21 to 69 years) with neglected fracture-dislocation of the PIP joint were included. The mean duration from injury to operation was 14.7 weeks (range, 3 to 66 weeks). The dorsolateral approach and extension block pinning were used to reduce dislocation. After thorough debridement of the scar tissues in the dorsal dead space and the fracture site, the reduction was maintained with transosseous wiring. Radiologic evaluations of bone union and arthritic changes and clinical evaluations (range of motion of the PIP joint and Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand [DASH] score) were performed. The mean follow-up period was 12.9 months (range, 12 to 19 months).
Results: All patients demonstrated evidence of radiographic healing within a mean healing time of 6 weeks (range, 4 to 10 weeks); however, one had a widened gap and one had an early arthritic change. The mean range of motion in the PIP joint was 81° (range, 50° to 105°). The mean DASH score was 21.6 (range, 7.5 to 35.8).
Conclusions: For chronic fracture-dislocation of the PIP joint, transosseous wiring with direct curettage and optimal bone purchase can provide satisfying outcome.
Keywords: Bone wires; Extension block; Fracture dislocation; Proximal interphalangeal joint.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A percutaneous technique to treat unstable dorsal fracture-dislocations of the proximal interphalangeal joint.J Hand Surg Am. 2011 Sep;36(9):1453-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2011.06.022. Epub 2011 Aug 6. J Hand Surg Am. 2011. PMID: 21820818
-
Percutaneous, intramedullary fracture reduction and extension block pinning for dorsal proximal interphalangeal fracture-dislocations.J Hand Surg Am. 2010 Dec;35(12):2046-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2010.08.004. Epub 2010 Oct 25. J Hand Surg Am. 2010. PMID: 20971582
-
Blocking Plate for Volar Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Fracture Dislocation.J Hand Surg Am. 2022 Sep;47(9):899.e1-899.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2021.07.025. Epub 2021 Sep 17. J Hand Surg Am. 2022. PMID: 34538670
-
Reverse Hemi-Hamate Autograft for Volar Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Fracture-Dislocations.J Hand Surg Am. 2023 Sep;48(9):956.e1-956.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2023.01.009. Epub 2023 Jul 29. J Hand Surg Am. 2023. PMID: 37516942 Review.
-
Management of Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Fracture Dislocations.Hand Clin. 2018 May;34(2):149-165. doi: 10.1016/j.hcl.2017.12.005. Hand Clin. 2018. PMID: 29625635 Review.
Cited by
-
Neglected Dorsal Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Dislocation Treated by Volar Plate Arthroplasty: A Case Series.Cureus. 2024 May 11;16(5):e60077. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60077. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38860079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shen XF, Mi JY, Rui YJ, et al. Delayed treatment of unstable proximal interphalangeal joint fracture-dislocations with a dynamic external fixator. Injury. 2015;46(10):1938–1944. - PubMed
-
- Weiss AP. Cerclage fixation for fracture dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(327):21–28. - PubMed
-
- Tang JB, Avanessian B. New tendon, nerve, and bone surgical methods impacting the practice of hand surgery. Clin Plast Surg. 2014;41(3):xix–xx. - PubMed
-
- Ng CY, Oliver CW. Fractures of the proximal interphalangeal joints of the fingers. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91(6):705–712. - PubMed
-
- Finsen V. Suzuki's pins and rubber traction for fractures of the base of the middle phalanx. J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2010;44(4-5):209–213. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

