Discovery, Characterisation, Engineering and Applications of Ene Reductases for Industrial Biocatalysis
- PMID: 31157123
- PMCID: PMC6542678
- DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.8b00624
Discovery, Characterisation, Engineering and Applications of Ene Reductases for Industrial Biocatalysis
Abstract
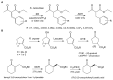
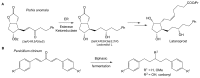
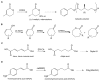
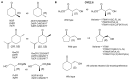
Recent studies of multiple enzyme families collectively referred to as ene-reductases (ERs) have highlighted potential industrial application of these biocatalysts in the production of fine and speciality chemicals. Processes have been developed whereby ERs contribute to synthetic routes as isolated enzymes, components of multi-enzyme cascades, and more recently in metabolic engineering and synthetic biology programmes using microbial cell factories to support chemicals production. The discovery of ERs from previously untapped sources and the expansion of directed evolution screening programmes, coupled to deeper mechanistic understanding of ER reactions, have driven their use in natural product and chemicals synthesis. Here we review developments, challenges and opportunities for the use of ERs in fine and speciality chemicals manufacture. The ER research field is rapidly expanding and the focus of this review is on developments that have emerged predominantly over the last 4 years.
Keywords: Ene-reductases; Old Yellow Enzymes; asymmetric alkene reduction; biocatalysis; synthetic biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Notes The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



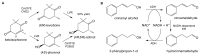
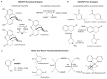




References
-
- Blamey JM, Fischer F, Meyer H-P, Sarmiento F, Zinn M. In: Biotechnology of Microbial Enzymes. Brahmachari G, Demain A, Adrio JL, editors. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA USA: 2017. pp. 347–403.
-
- Honda K. In: Biotechnology of Microbial Enzymes. Brahmachari G, Demain A, Adrio JL, editors. Vol. 16. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA USA: 2017. pp. 433–450.
-
- Kataoka M, Miyakawa T, Shimizu S, Tanokura M. Enzymes useful for chiral compound synthesis: structural biology, directed evolution, and protein engineering for industrial use. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;100:5747–5757. - PubMed
-
- Vidal LS, Kelly CL, Mordaka PM, Heap JT. Review of NAD(P)H-dependent oxidoreductases: Properties, engineering and application. Biochim Biophys Acta, Proteins Proteomics. 2018;1866:327–347. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
