Emergent Invasive Group A Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis, United States, 2015-2018
- PMID: 31158071
- PMCID: PMC6649341
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2508.181758
Emergent Invasive Group A Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis, United States, 2015-2018
Abstract
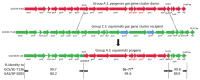
The term group A Streptococcus is considered synonymous for the species Streptococcus pyogenes. We describe an emergent invasive S. dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis lineage that obtained the group A antigen through a single ancestral recombination event between a group C S. dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis strain and a group A S. pyogenes strain.
Keywords: ABCs; Active Bacterial Core surveillance; GAS; Lancefield group A antigen; Streptococccus equisimilis; Streptococcus dysgalactiae; Streptococcus pyogenes; bacteria; bacterial infections; invasive group A Streptococcus; multilocus sequence type; streptococci.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetic relationships deduced from emm and multilocus sequence typing of invasive Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis and S. canis recovered from isolates collected in the United States.J Clin Microbiol. 2009 Jul;47(7):2046-54. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00246-09. Epub 2009 Apr 22. J Clin Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19386831 Free PMC article.
-
Six-month multicenter study on invasive infections due to Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis in Argentina.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Feb;43(2):802-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.2.802-807.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15695683 Free PMC article.
-
Necrotizing soft tissue infections caused by Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis of groups C and G in western Norway.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013 Dec;19(12):E545-50. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12276. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013. PMID: 23795951
-
Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis bacteremia: an emerging infection.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014 Aug;33(8):1303-10. doi: 10.1007/s10096-014-2092-0. Epub 2014 Mar 29. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24682845 Review.
-
Intra-familial transmission of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis (SDSE): A first case report and review of the literature.J Infect Chemother. 2022 Jun;28(6):819-822. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2022.01.017. Epub 2022 Feb 1. J Infect Chemother. 2022. PMID: 35115237 Review.
Cited by
-
The intricate pathogenicity of Group A Streptococcus: A comprehensive update.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2412745. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2412745. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 39370779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic analysis reveals the genetic diversity and zoonotic potential of Streptococcus dysgalactiae isolates from sheep.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 25;15(1):3165. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87781-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39863800 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of intra-partum azithromycin on carriage of group A streptococcus in the Gambia: a posthoc analysis of a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial.BMC Infect Dis. 2022 Jan 29;22(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07080-4. BMC Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35093029 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Streptokinase reduces Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis biofilm formation.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Sep 30;24(1):378. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03540-w. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39350011 Free PMC article.
-
Inter-species gene flow drives ongoing evolution of Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 13;15(1):2286. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46530-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38480728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tanaka D, Isobe J, Watahiki M, Nagai Y, Katsukawa C, Kawahara R, et al.; Working Group for Group A Streptococci in Japan. Genetic features of clinical isolates of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis possessing Lancefield’s group A antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46:1526–9. 10.1128/JCM.02188-07 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmad Y, Gertz RE Jr, Li Z, Sakota V, Broyles LN, Van Beneden C, et al. Genetic relationships deduced from emm and multilocus sequence typing of invasive Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis and S. canis recovered from isolates collected in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:2046–54. 10.1128/JCM.00246-09 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

