Protein phosphatase 2A as a therapeutic target in inflammation and neurodegeneration
- PMID: 31158394
- PMCID: PMC6700395
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.05.016
Protein phosphatase 2A as a therapeutic target in inflammation and neurodegeneration
Abstract
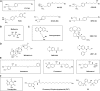
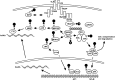
Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) is a highly complex heterotrimeric enzyme that catalyzes the selective removal of phosphate groups from protein serine and threonine residues. Emerging evidence suggests that it functions as a tumor suppressor by constraining phosphorylation-dependent signalling pathways that regulate cellular transformation and metastasis. Therefore, PP2A-activating drugs (PADs) are being actively sought and investigated as potential novel anti-cancer treatments. Here we explore the concept that PP2A also constrains inflammatory responses through its inhibitory effects on various signalling pathways, suggesting that PADs may be effective in the treatment of inflammation-mediated pathologies.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Cancer; Inflammation; Multiple sclerosis; Neurodegeneration; Protein phosphatase 2A.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Abraham S.M., Clark A.R. Dual-specificity phosphatase 1: A critical regulator of innate immune responses. Biochemical Society Transactions. 2006;34:1018–1023. - PubMed
-
- Airas L., Dickens A.M., Elo P., Marjamaki P., Johansson J., Eskola O.…Rinne J. In vivo PET imaging demonstrates diminished microglial activation after fingolimod treatment in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 2015;56:305–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

