Small molecule ONC201 inhibits HIV-1 replication in macrophages via FOXO3a and TRAIL
- PMID: 31158413
- PMCID: PMC6620139
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2019.05.015
Small molecule ONC201 inhibits HIV-1 replication in macrophages via FOXO3a and TRAIL
Abstract
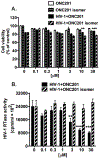
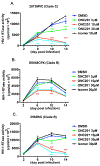
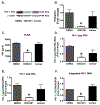
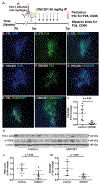
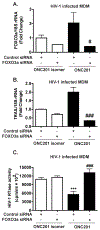
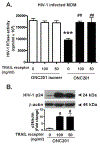
Despite the success of antiretroviral therapy (ART), eradication of HIV-1 from brain reservoirs remains elusive. HIV-1 brain reservoirs include perivascular macrophages that are behind the blood-brain barrier and difficult to access by ART. Macrophages express transcription factor FOXO3a and the TNF superfamily cytokine TRAIL, which are known to target HIV-1-infected macrophages for viral inhibition. ONC201 is a novel and potent FOXO3a activator capable of inducing TRAIL. It can cross the blood-brain barrier, and has shown antitumor effects in clinical trials. We hypothesized that activation of FOXO3a/TRAIL by ONC201 will inhibit HIV-1 replication in macrophages. Using primary human monocyte-derived macrophages, we demonstrated that ONC201 dose-dependently decreased replication levels of both HIV-1 laboratory strain and primary strains as determined by HIV-1 reverse transcriptase activity assay. Consistent with data on HIV-1 replication, ONC201 also reduced intracellular and extracellular p24, viral RNA, and integrated HIV-1 DNA in infected macrophages. Blocking TRAIL or knockdown of FOXO3a with siRNA reversed ONC201-mediated HIV-1 suppression, suggesting that ONC201 inhibits HIV-1 through FOXO3a and TRAIL. The anti-HIV-1 effect of ONC201 was further validated in vivo in NOD/scid-IL-2Rgcnull mice. After intracranial injection of HIV-1-infected macrophages into the basal ganglia, we treated the mice daily with ONC201 through intraperitoneal injection for six days. ONC201 significantly decreased p24 levels in both the macrophages and the brain tissues, suggesting that ONC201 suppresses HIV-1 in vivo. Therefore, ONC201 can be a promising drug candidate to combat persistent HIV-1 infection in the brain.
Keywords: FOXO3a; HIV-1; Macrophages; ONC201; Reservoir; TRAIL.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Small-Molecule ONC201/TIC10 Targets Chemotherapy-Resistant Colorectal Cancer Stem-like Cells in an Akt/Foxo3a/TRAIL-Dependent Manner.Cancer Res. 2015 Apr 1;75(7):1423-32. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3451. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25712124 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of TRAIL-inducing compounds highlights small molecule ONC201/TIC10 as a unique anti-cancer agent that activates the TRAIL pathway.Mol Cancer. 2015 May 1;14:99. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0346-9. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25927855 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced antiretroviral drug efficacy and concentration in HIV-infected microglia contributes to viral persistence in brain.Retrovirology. 2017 Oct 16;14(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12977-017-0370-5. Retrovirology. 2017. PMID: 29037245 Free PMC article.
-
ONC201 and imipridones: Anti-cancer compounds with clinical efficacy.Neoplasia. 2020 Dec;22(12):725-744. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2020.09.005. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Neoplasia. 2020. PMID: 33142238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms underlying of antiretroviral drugs in different cellular reservoirs with a focus on macrophages.Virulence. 2020 Dec;11(1):400-413. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1760443. Virulence. 2020. PMID: 32375558 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Suppression of HIV in Myeloid Cells by the BRD4-Selective Small Molecule Modulator ZL0580.J Virol. 2020 May 18;94(11):e01880-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01880-19. Print 2020 May 18. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32188727 Free PMC article.
-
The mitochondrial protease ClpP is a druggable target that controls VSMC phenotype by a SIRT1-dependent mechanism.Redox Biol. 2024 Jul;73:103203. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103203. Epub 2024 May 21. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38823208 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNA Metastasis-Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 Promotes HIV-1 Replication through Modulating microRNAs in Macrophages.J Virol. 2023 Jun 29;97(6):e0005323. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00053-23. Epub 2023 May 31. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37255470 Free PMC article.
-
FOXO3a inhibits nephroblastoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and induces apoptosis through downregulating the Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Nov;24(5):796. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12436. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34515328 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-Infected Macrophages Are Infected and Killed by the Interferon-Sensitive Rhabdovirus MG1.J Virol. 2021 Apr 12;95(9):e01953-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01953-20. Print 2021 Apr 12. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33568507 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen JE, Kline CL, Prabhu VV, Wagner J, Ishizawa J, Madhukar N, Lev A, Baumeister M, Zhou L, Lulla A, Stogniew M, Schalop L, Benes C, Kaufman HL, Pottorf RS, Nallaganchu BR, Olson GL, Al-Mulla F, Duvic M, Wu GS, Dicker DT, Talekar MK, Lim B, Elemento O, Oster W, Bertino J, Flaherty K, Wang ML, Borthakur G, Andreeff M, Stein M, El-Deiry WS, 2016. Discovery and clinical introduction of first-in-class imipridone ONC201. Oncotarget 7, 74380–74392. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen JE, Krigsfeld G, Mayes PA, Patel L, Dicker DT, Patel AS, Dolloff NG, Messaris E, Scata KA, Wang W, Zhou JY, Wu GS, El-Deiry WS, 2013. Dual inactivation of Akt and ERK by TIC10 signals Foxo3a nuclear translocation, TRAIL gene induction, and potent antitumor effects. Sci Transl Med 5, 171ra117. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Archin NM, Liberty AL, Kashuba AD, Choudhary SK, Kuruc JD, Crooks AM, Parker DC, Anderson EM, Kearney MF, Strain MC, Richman DD, Hudgens MG, Bosch RJ, Coffin JM, Eron JJ, Hazuda DJ, Margolis DM, 2012. Administration of vorinostat disrupts HIV-1 latency in patients on antiretroviral therapy. Nature 487, 482–485. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

