Sea Anemone Toxins: A Structural Overview
- PMID: 31159357
- PMCID: PMC6627431
- DOI: 10.3390/md17060325
Sea Anemone Toxins: A Structural Overview
Abstract
Sea anemones produce venoms of exceptional molecular diversity, with at least 17 different molecular scaffolds reported to date. These venom components have traditionally been classified according to pharmacological activity and amino acid sequence. However, this classification system suffers from vulnerabilities due to functional convergence and functional promiscuity. Furthermore, for most known sea anemone toxins, the exact receptors they target are either unknown, or at best incomplete. In this review, we first provide an overview of the sea anemone venom system and then focus on the venom components. We have organised the venom components by distinguishing firstly between proteins and non-proteinaceous compounds, secondly between enzymes and other proteins without enzymatic activity, then according to the structural scaffold, and finally according to molecular target.
Keywords: cytotoxin; enzyme; molecular scaffold; neurotoxin; sea anemone; toxin; venom.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures



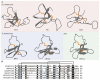




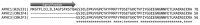



References
-
- Brusca R.C., Brusca G.J., Haver N. Invertebrates. 2nd ed. Sinauer Associates; Sunderland, MA, USA: 2003.
-
- Galliot B., Schmid V. Cnidarians as a model system for understanding evolution and regeneration. Int J. Dev. Biol. 2002;46:39–48. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez E., Barbeitos M.S., Brugler M.R., Crowley L.M., Grajales A., Gusmao L., Haussermann V., Reft A., Daly M. Hidden among sea anemones: the first comprehensive phylogenetic reconstruction of the order Actiniaria (Cnidaria, Anthozoa, Hexacorallia) reveals a novel group of hexacorals. PLoS One. 2014;9:e96998. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096998. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shick J.M. A Functional Biology of Sea Anemones. Chapman & Hall; London, UK: 1991.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

