The little tissue that couldn't - dispelling myths about the Hymen's role in determining sexual history and assault
- PMID: 31159818
- PMCID: PMC6547601
- DOI: 10.1186/s12978-019-0731-8
The little tissue that couldn't - dispelling myths about the Hymen's role in determining sexual history and assault
Abstract
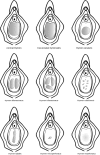
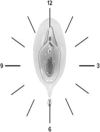
Conclusions about women's and girls' sexual history are made in some settings based on assumptions about the hymen, a small membranous tissue with no known biological function, which typically occupies a portion of the external vaginal opening in females. Clinicians, however, continue to refer to changes in the hymen to assess for a history of consensual or nonconsensual sexual intercourse. We reviewed published evidence to dispel commonly held myths about the hymen and its morphology, function, and use as evidence in cases of sexual violence.An examination of the hymen is not an accurate or reliable test of a previous history of sexual activity, including sexual assault. Clinicians tasked with performing forensic sexual assault examinations should avoid descriptions such as "intact hymen" or "broken hymen" in all cases, and describe specific findings using international standards and terminology of morphological features.We call on clinicians to consider the low predictive value of a hymen examination and to: 1) avoid relying solely on the status of the hymen in sexual assault examinations and reporting; 2) help raise awareness of this issue among their peers and counterparts in law enforcement and the judicial system; and 3) promote fact-based discussions about the limitations of hymenal examinations as part of clinical education for all specialties that address the sexual or reproductive health of women and girls.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Schuster S. Hymen restoration: “my” discomfort, “their” culture, and Women’s missing voice. J Clin Ethics. 2015;26(2):162–165. - PubMed
-
- Eich T. A tiny membrane defending “us” against “them”: Arabic internet debate about hymenorraphy in Sunni Islamic law. Cult Health Sex. 2010;12(7):755–769. - PubMed
-
- Hobday AJ, Haury L, Dayton PK. Function of the human hymen. Med Hypotheses. 1997;49(2):171–173. - PubMed
-
- What’s the Purpose of the Human Hymen? | DiscoverMagazine.com. (n.d.). Retrieved February 18, 2019, from http://discovermagazine.com/2014/nov/3-ask-discover
-
- Independent Forensic Expert Group Statement on virginity testing. J Forensic Legal Med. 2015;33:121–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous