The insulin receptor goes nuclear
- PMID: 31160720
- PMCID: PMC6796868
- DOI: 10.1038/s41422-019-0185-0
The insulin receptor goes nuclear
Figures
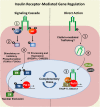
Comment on
-
Insulin Receptor Associates with Promoters Genome-wide and Regulates Gene Expression.Cell. 2019 Apr 18;177(3):722-736.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.02.030. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Cell. 2019. PMID: 30955890 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

