The CURE for Cultivating Fastidious Microbes
- PMID: 31160939
- PMCID: PMC6508911
- DOI: 10.1128/jmbe.v20i1.1635
The CURE for Cultivating Fastidious Microbes
Abstract
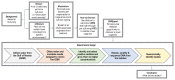
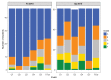
Course-Based Undergraduate Research Experiences (CUREs) expand the scientific educational benefits of research to large groups of students in a course setting. As part of an ongoing effort to integrate CUREs into first-year biology labs, we developed a microbiology CURE (mCURE) that uses a modified dilution-to-extinction high throughput culturing protocol for isolating abundant yet fastidious aquatic bacterioplankton during one semester. Students learn common molecular biology techniques like nucleic acid extraction, PCR, and molecular characterization; read and evaluate scientific literature; and receive training in scientific communication through written and oral exercises that incorporate social media elements. In the first three semesters, the mCUREs achieved similar cultivability success as implementation of the protocol in a standard laboratory setting. Our modular framework facilitates customization of the curriculum for use in multiple settings and we provide classroom exercises, assignments, assessment tools, and examples of student output to assist with implementation.
Figures

References
-
- Brownell SE, Hekmat-Scafe DS, Singla V, Chandler Seawell P, Conklin Imam JF, Eddy SL, Stearns T, Cyert MS. A high-enrollment course-based undergraduate research experience improves student conceptions of scientific thinking and ability to interpret data. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2015;14(2):ar21. doi: 10.1187/cbe.14-05-0092. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Olimpo JT, Fisher GR, DeChenne-Peters SE. Development and evaluation of the tigriopus course-based undergraduate research experience: impacts on students’ content knowledge, attitudes, and motivation in a majors introductory biology course. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2016;15(4):ar72. doi: 10.1187/cbe.15-11-0228. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shapiro C, Moberg-Parker J, Toma S, Ayon C, Zimmerman H, Roth-Johnson EA, Hancock SP, Levis-Fitzgerald M, Sanders ER. Comparing the impact of course-based and apprentice-based research experiences in a life science laboratory curriculum. J Microbiol Biol Educ. 2015;16:186–197. doi: 10.1128/jmbe.v16i2.1045. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
