Case Report: Spontaneous Resolution of Intracavitary Hepatic Artery Pseudoaneurysm Caused by Amebic Liver Abscess following Percutaneous Drainage
- PMID: 31162010
- PMCID: PMC6609167
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.19-0103
Case Report: Spontaneous Resolution of Intracavitary Hepatic Artery Pseudoaneurysm Caused by Amebic Liver Abscess following Percutaneous Drainage
Abstract
Intrahepatic pseudoaneurysm (IHPA) is generally iatrogenic, and it warrants urgent management because of its reportedly significant risk of rupture leading to considerable mortality. Intrahepatic pseudoaneurysm caused by amebic liver abscess (ALA) is exceedingly rare with fewer than seven published reports. All reported symptomatic cases have been treated with hepatic artery embolization; therefore, little is known about its natural course and effect of abscess drainage on its outcome. We report the first case of symptomatic intracavitary IHPA caused by ALA in which ultrasound-guided percutaneous catheter drainage of the abscess resulted in the spontaneous resolution of the IHPA.
Figures

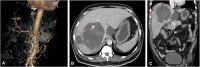
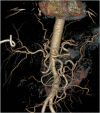
References
-
- Tulsyan N, Kashyap VS, Greenberg RK, Sarac TP, Clair DG, Pierce G, Ouriel K, 2007. The endovascular management of visceral artery aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms. J Vasc Surg 45: 276–283. - PubMed
-
- Berceli SA, 2005. Hepatic and splenic artery aneurysms. Semin Vasc Surg 18: 196–201. - PubMed
-
- Green MH, Duell RM, Johnson CD, Jamieson NV, 2001. Haemobilia. Br J Surg 88: 773–786. - PubMed
-
- Tessier DJ, Fowl RJ, Stone WM, McKusick MA, Abbas MA, Sarr MG, Nagorney DM, Cherry KJ, Gloviczki P, 2003. Iatrogenic hepatic artery pseudoaneurysms: an uncommon complication after hepatic, biliary, and pancreatic procedures. Ann Vasc Surg 17: 663–669. - PubMed
-
- Gopanpallikar A, Rathi P, Sawant P, Gupta R, Dhadphale S, Deshmukh H, 1997. Hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm associated with amebic liver abscess presenting as upper GI hemorrhage. Am J Gastroenterol 92: 1391–1393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

