Effect of a Home-Based Exercise Program on Subsequent Falls Among Community-Dwelling High-Risk Older Adults After a Fall: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 31162569
- PMCID: PMC6549299
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2019.5795
Effect of a Home-Based Exercise Program on Subsequent Falls Among Community-Dwelling High-Risk Older Adults After a Fall: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Erratum in
-
Omitted Conflict of Interest Disclosures.JAMA. 2019 Jul 9;322(2):174. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.9011. JAMA. 2019. PMID: 31287508 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: Whether exercise reduces subsequent falls in high-risk older adults who have already experienced a fall is unknown.
Objective: To assess the effect of a home-based exercise program as a fall prevention strategy in older adults who were referred to a fall prevention clinic after an index fall.
Design, setting, and participants: A 12-month, single-blind, randomized clinical trial conducted from April 22, 2009, to June 5, 2018, among adults aged at least 70 years who had a fall within the past 12 months and were recruited from a fall prevention clinic.
Interventions: Participants were randomized to receive usual care plus a home-based strength and balance retraining exercise program delivered by a physical therapist (intervention group; n = 173) or usual care, consisting of fall prevention care provided by a geriatrician (usual care group; n = 172). Both were provided for 12 months.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome was self-reported number of falls over 12 months. Adverse event data were collected in the exercise group only and consisted of falls, injuries, or muscle soreness related to the exercise intervention.
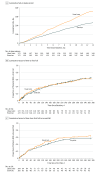
Results: Among 345 randomized patients (mean age, 81.6 [SD, 6.1] years; 67% women), 296 (86%) completed the trial. During a mean follow-up of 338 (SD, 81) days, a total of 236 falls occurred among 172 participants in the exercise group vs 366 falls among 172 participants in the usual care group. Estimated incidence rates of falls per person-year were 1.4 (95% CI, 0.1-2.0) vs 2.1 (95% CI, 0.1-3.2), respectively. The absolute difference in fall incidence was 0.74 (95% CI, 0.04-1.78; P = .006) falls per person-year and the incident rate ratio was 0.64 (95% CI, 0.46-0.90; P = .009). No adverse events related to the intervention were reported.
Conclusions and relevance: Among older adults receiving care at a fall prevention clinic after a fall, a home-based strength and balance retraining exercise program significantly reduced the rate of subsequent falls compared with usual care provided by a geriatrician. These findings support the use of this home-based exercise program for secondary fall prevention but require replication in other clinical settings.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifiers: NCT01029171; NCT00323596.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Falls in Older Adults: Prevention, Mortality, and Costs.JAMA. 2019 Jun 4;321(21):2080-2081. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.6569. JAMA. 2019. PMID: 31162553 No abstract available.
-
Exercise to Prevent Falls in Older Adults.JAMA. 2019 Oct 8;322(14):1415. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.12184. JAMA. 2019. PMID: 31593264 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gillespie LD, Robertson MC, Gillespie WJ, et al. . Interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;(2):CD007146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

