Stereochemistry and innate immune recognition: (+)-norbinaltorphimine targets myeloid differentiation protein 2 and inhibits toll-like receptor 4 signaling
- PMID: 31162938
- PMCID: PMC6988860
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201900173RRR
Stereochemistry and innate immune recognition: (+)-norbinaltorphimine targets myeloid differentiation protein 2 and inhibits toll-like receptor 4 signaling
Abstract
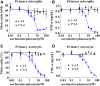
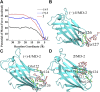
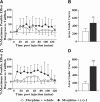
Deregulation of innate immune TLR4 signaling contributes to various diseases including neuropathic pain and drug addiction. Naltrexone is one of the rare TLR4 antagonists with good blood-brain barrier permeability and showing no stereoselectivity for TLR4. By linking 2 naltrexone units through a rigid pyrrole spacer, the bivalent ligand norbinaltorphimine was formed. Interestingly, (+)-norbinaltorphimine [(+)-1] showed ∼25 times better TLR4 antagonist activity than naltrexone in microglial BV-2 cell line, whereas (-)-norbinaltorphimine [(-)-1] lost TLR4 activity. The enantioselectivity of norbinaltorphimine was further confirmed in primary microglia, astrocytes, and macrophages. The activities of meso isomer of norbinaltorphimine and the molecular dynamic simulation results demonstrate that the stereochemistry of (+)-1 is derived from the (+)-naltrexone pharmacophore. Moreover, (+)-1 significantly increased and prolonged morphine analgesia in vivo. The efficacy of (+)-1 is long lasting. This is the first report showing enantioselective modulation of the innate immune TLR signaling.-Zhang, X., Peng, Y., Grace, P. M., Metcalf, M. D., Kwilasz, A. J., Wang, Y., Zhang, T., Wu, S., Selfridge, B. R., Portoghese, P. S., Rice, K. C., Watkins, L. R., Hutchinson, M. R., Wang, X. Stereochemistry and innate immune recognition: (+)-norbinaltorphimine targets myeloid differentiation protein 2 and inhibits toll-like receptor 4 signaling.
Keywords: MD-2; TLR4; enantioselective modulation; morphine analgesia; norbinaltorphimine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors thank the Drug Supply Program of National Institute of Drug Abuse (Bethesda, MD, USA) for providing (−)-norbinaltorphimine. The authors also thank the Network and Coumputing Center, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, National Supercomputer Center of China in Guangzhou and the Computing Center of Jilin Province for the supply of computational resources. This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0800907), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21850410455, 21750110432, 21877106), the 100 Talents Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Young Talents Program of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (NO.1610342016013), Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province (20180101021JC), Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, Nanjing University (Grant No. KF-GN-201601), and U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research Grant R01 DE017782 (to L.R.W.). The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Rifampin inhibits Toll-like receptor 4 signaling by targeting myeloid differentiation protein 2 and attenuates neuropathic pain.FASEB J. 2013 Jul;27(7):2713-22. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-222992. Epub 2013 Apr 8. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23568774 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the Innate Immune Recognition of Opioid Inactive Isomer (+)-Naltrexone Derived Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Antagonists.J Chem Inf Model. 2018 Apr 23;58(4):816-825. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.7b00717. Epub 2018 Apr 11. J Chem Inf Model. 2018. PMID: 29518316 Free PMC article.
-
Nalmefene non-enantioselectively targets myeloid differentiation protein 2 and inhibits toll-like receptor 4 signaling: wet-lab techniques and in silico simulations.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2021 Jun 2;23(21):12260-12269. doi: 10.1039/d1cp00237f. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2021. PMID: 34013938
-
Pharmacological characterization of the opioid inactive isomers (+)-naltrexone and (+)-naloxone as antagonists of toll-like receptor 4.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Mar;173(5):856-69. doi: 10.1111/bph.13394. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26603732 Free PMC article.
-
Lovastatin inhibits Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in microglia by targeting its co-receptor myeloid differentiation protein 2 and attenuates neuropathic pain.Brain Behav Immun. 2019 Nov;82:432-444. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.09.013. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Brain Behav Immun. 2019. PMID: 31542403
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Studying Toll-like Receptors with the Use of Computational Methods.J Chem Inf Model. 2023 Jun 26;63(12):3669-3687. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.3c00419. Epub 2023 Jun 7. J Chem Inf Model. 2023. PMID: 37285179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-like Receptors and Thrombopoiesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 5;24(2):1010. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021010. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4)/Opioid Receptor Pathway Crosstalk and Impact on Opioid Analgesia, Immune Function, and Gastrointestinal Motility.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 8;11:1455. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01455. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32733481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nicotine and its metabolite cotinine target MD2 and inhibit TLR4 signaling.Innovation (Camb). 2021 Apr 30;2(2):100111. doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100111. eCollection 2021 May 28. Innovation (Camb). 2021. PMID: 34557761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takeuchi O., Akira S. (2010) Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 140, 805–820 - PubMed
-
- Yang H., Hreggvidsdottir H. S., Palmblad K., Wang H., Ochani M., Li J., Lu B., Chavan S., Rosas-Ballina M., Al-Abed Y., Akira S., Bierhaus A., Erlandsson-Harris H., Andersson U., Tracey K. J. (2010) A critical cysteine is required for HMGB1 binding to Toll-like receptor 4 and activation of macrophage cytokine release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 11942–11947 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hutchinson M. R., Northcutt A. L., Hiranita T., Wang X., Lewis S. S., Thomas J., van Steeg K., Kopajtic T. A., Loram L. C., Sfregola C., Galer E., Miles N. E., Bland S. T., Amat J., Rozeske R. R., Maslanik T., Chapman T. R., Strand K. A., Fleshner M., Bachtell R. K., Somogyi A. A., Yin H., Katz J. L., Rice K. C., Maier S. F., Watkins L. R. (2012) Opioid activation of toll-like receptor 4 contributes to drug reinforcement. J. Neurosci. 32, 11187–11200 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

