Theoretical integration of user satisfaction and technology acceptance of the nursing process information system
- PMID: 31163076
- PMCID: PMC6548361
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217622
Theoretical integration of user satisfaction and technology acceptance of the nursing process information system
Abstract
Background: The nursing process system (NPS) is used to establish the nursing process involving assessment, diagnosis, planning, intervention, and evaluation in solving the health problems of patients.
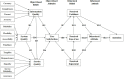
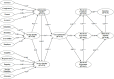
Objectives: The factors influencing the use of the NPS by nurses were analyzed based on user satisfaction and technology acceptance within the 3Q (service quality, information quality, and system quality) model.
Methods: In this cross-sectional quantitative study, the valid responses of 222 nurses to a questionnaire were obtained; these nurses worked at eight hospitals affiliated with public organizations in Taiwan. Structural equation modeling was used to analyze information quality, system quality, service quality, user satisfaction, perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, perceived enjoyment, behavioral attitude, and intention after the nurses had used the NPS system for more than 1 month.
Results: Information quality, service quality, and system quality influenced user satisfaction. User satisfaction affected perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and perceived enjoyment and had the highest explanatory power (R2 = 0.75). Furthermore, perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and perceived enjoyment influenced behavioral attitude and intention to use the system. The proposed model explained 53% of the variance in the intention to use the NPS.
Conclusions: The relationships between the variables of the 3Q model were successfully used to examine the intention of nurses toward using the NPS. Using the findings of this study, designers and programmers can comprehensively understand the perceptions of nurses and further improve the performance of the NPS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Hussey P, Adams E, Shaffer FA. Nursing Informatics and Leadership, an Essential Competency for a Global Priority: eHealth. 2015;13(5):52–7. 10.1016/j.mnl.2015.07.002. - DOI
-
- Ho KF. Building a Knowledge-Based Decision Support System according to NANDA, NOC, and NIC Standard in Nursing Process for Psychiatric Mental Health Department(in chinese). Taipei, Taiwan, ROC: Taipei Medical university; 2009.
-
- Tsai HH, Chiou SF, Wang TC, Wu MP, Feng RC. An Empirical Study on the Successful Implementation of Nursing Information System. Studies in health technology and informatics. 2016;225:846–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources