Steroid receptor/coactivator binding inhibitors: An update
- PMID: 31163202
- PMCID: PMC6645384
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2019.110471
Steroid receptor/coactivator binding inhibitors: An update
Abstract
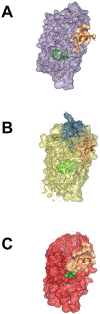
The purpose of this review is to highlight recent developments in small molecules and peptides that block the binding of coactivators to steroid receptors. These coactivator binding inhibitors bind at the coregulator binding groove, also known as Activation Function-2, rather than at the ligand-binding site of steroid receptors. Steroid receptors that have been targeted with coactivator binding inhibitors include the androgen receptor, estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor. Coactivator binding inhibitors may be useful in some cases of resistance to currently prescribed therapeutics. The scope of the review includes small-molecule and peptide coactivator binding inhibitors for steroid receptors, with a particular focus on recent compounds that have been assayed in cell-based models.
Keywords: Androgen receptor; Coactivator binding inhibitors; Estrogen receptor; Progesterone receptor; Protein-protein interactions; Steroid receptor coactivator.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

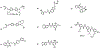


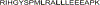
References
-
- Aarts JMMJG, Wang S, Houtman R, Van Beuningen RMGJ, Westerink WMA, Van De Waart BJ, Rietjens IMCM, Bovee TFH, 2013. Robust array-based coregulator binding assay predicting ERα-agonist potency and generating binding profiles reflecting ligand structure. Chem. Res. Toxicol 26, 336–346. 10.1021/tx300463b - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

