Multicomponent reactions (MCRs): a useful access to the synthesis of benzo-fused γ-lactams
- PMID: 31164944
- PMCID: PMC6541321
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.15.104
Multicomponent reactions (MCRs): a useful access to the synthesis of benzo-fused γ-lactams
Abstract
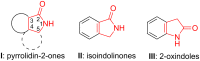
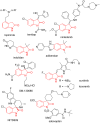
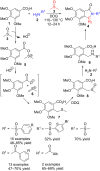
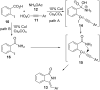
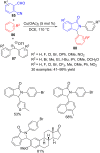
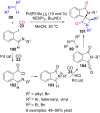
Benzo-fused γ-lactam rings such as isoindolin-2-ones and 2-oxindoles are part of the structure of many pharmaceutically active molecules. They can be often synthesized by means of multicomponent approaches and recent contributions in this field are summarized in this review. Clear advantages of these methods include the efficiency in saving raw materials and working time. However, there is still a need of new catalytic systems to allow the enantioselective preparation of these heterocycles by multicomponent reactions.
Keywords: 2-oxindoles; indolin-2-ones; isoindolinones; multicomponent reactions; γ-lactams.
Figures
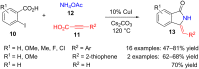
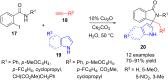
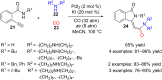
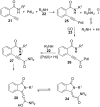
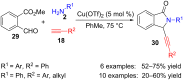
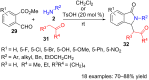
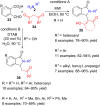
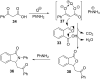


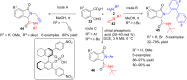

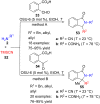
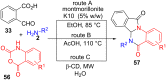
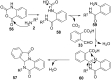
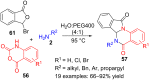
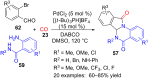
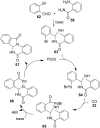
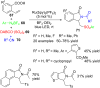


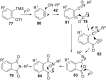

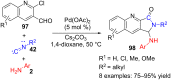
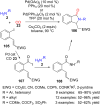
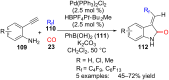
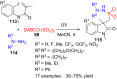
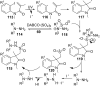
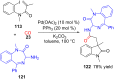
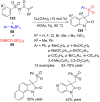
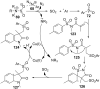
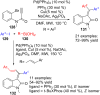
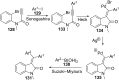
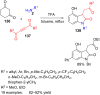
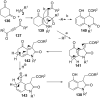
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
