Longevity Effect of Liuwei Dihuang in Both Caenorhabditis Elegans and Aged Mice
- PMID: 31165002
- PMCID: PMC6538212
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2018.0604
Longevity Effect of Liuwei Dihuang in Both Caenorhabditis Elegans and Aged Mice
Abstract
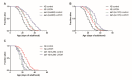
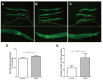
Liuwei Dihuang (LWDH), a famous traditional Chinese medicine, is widely used in the clinical treatment of aging-related diseases in China. However, its pharmacological mechanisms are not clear. In the present study, we evaluated the lifespan extension effect of LWDH in C. elegans and mice and revealed its underlying mechanisms. The results showed that LWDH significantly extended the lifespan of C. elegans in a dose-dependent manner. LWDH also conferred protection to nematodes against oxidative stress and reduced their fat storage. Genetics analysis and microarray data showed that the longevity effect of LWDH was attributed to the regulation of the innate immune response, proteolysis, lipid metabolism, and the oxidation-reduction process and was dependent on daf-16. Among the six herbs in the formula, Radix Rehmanniae Preparata and Fructus Macrocarpii contributed most to the longevity effect of this medicine, while the other four components had a synergistic effect on the longevity effect of the prescription. The lack of any single herb reduced the efficacy of the complete formula. LWDH also extended the lifespan and reduced both the weight and oxidant stress status in aged mice. Taken together, these results suggested that LWDH might function in a multi-target manner to extend the lifespan in both C. elegans and aged mice, and the best effect was achieved with the complete formula.
Keywords: lifespan; microarray; model organisms; signal pathway; traditional Chinese medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Perry B, Zhang J, Saleh T, Wang Y (2014). Liuwei Dihuang, a traditional Chinese herbal formula, suppresses chronic inflammation and oxidative stress in obese rats. J Integr Med, 12:447-454. - PubMed
-
- Lee, Kwang-Sik, Lim, Baek-Vin, Chang, Hyun-Kyung, et al. (2005). Liuweidihuang-tang improves spatial memory function and increases neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus in rats. Fitoterapia, 76:514-519. - PubMed
-
- Huang Y, Zhang H, Yang S, Qiao H, Zhou W, Zhang Y (2012). Liuwei Dihuang decoction facilitates the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) in senescence accelerated mouse/prone 8 (SAMP8) hippocampal slices by inhibiting voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) and promoting N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDA) receptors. J Ethnopharmacol, 140:384-390. - PubMed
-
- Dai B, Wu Q, Zeng C, Zhang J, Cao L, Xiao Z, et al. (2016). The effect of Liuwei Dihuang decoction on PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in liver of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) rats with insulin resistance. J Ethnopharmacol, 192:382-389. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
