Access to and delivery of acute ischaemic stroke treatments: A survey of national scientific societies and stroke experts in 44 European countries
- PMID: 31165091
- PMCID: PMC6533860
- DOI: 10.1177/2396987318786023
Access to and delivery of acute ischaemic stroke treatments: A survey of national scientific societies and stroke experts in 44 European countries
Abstract
Introduction: Acute stroke unit care, intravenous thrombolysis and endovascular treatment significantly improve the outcome for patients with ischaemic stroke, but data on access and delivery throughout Europe are lacking. We assessed best available data on access and delivery of acute stroke unit care, intravenous thrombolysis and endovascular treatment throughout Europe.
Methods: A survey, drafted by stroke professionals (ESO, ESMINT, EAN) and a patient organisation (SAFE), was sent to national stroke societies and experts in 51 European countries (World Health Organization definition) requesting experts to provide national data on stroke unit, intravenous thrombolysis and endovascular treatment rates. We compared both pooled and individual national data per one million inhabitants and per 1000 annual incident ischaemic strokes with highest country rates. Population estimates were based on United Nations data, stroke incidences on the Global Burden of Disease Report.
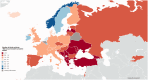
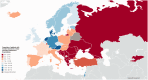
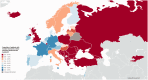
Results: We obtained data from 44 European countries. The estimated mean number of stroke units was 2.9 per million inhabitants (95% CI 2.3-3.6) and 1.5 per 1000 annual incident strokes (95% CI 1.1-1.9), highest country rates were 9.2 and 5.8. Intravenous thrombolysis was provided in 42/44 countries. The estimated mean annual number of intravenous thrombolysis was 142.0 per million inhabitants (95% CI 107.4-176.7) and 72.7 per 1000 annual incident strokes (95% CI 54.2-91.2), highest country rates were 412.2 and 205.5. Endovascular treatment was provided in 40/44 countries. The estimated mean annual number of endovascular treatments was 37.1 per million inhabitants (95% CI 26.7-47.5) and 19.3 per 1000 annual incident strokes (95% CI 13.5-25.1), highest country rates were 111.5 and 55.9. Overall, 7.3% of incident ischaemic stroke patients received intravenous thrombolysis (95% CI 5.4-9.1) and 1.9% received endovascular treatment (95% CI 1.3-2.5), highest country rates were 20.6% and 5.6%.
Conclusion: We observed major inequalities in acute stroke treatment between and within 44 European countries. Our data will assist decision makers implementing tailored stroke care programmes for reducing stroke-related morbidity and mortality in Europe.
Keywords: Europe; Survey; acute stroke treatment; endovascular treatment; health care resources; intravenous thrombolysis; stroke unit.
Figures



Comment in
-
Status and Perspectives of Acute Stroke Care in Europe.Stroke. 2018 Oct;49(10):2281-2282. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.022992. Stroke. 2018. PMID: 30355133 No abstract available.
References
-
- European Heart Network. European cardiovascular disease statistics. Brussels: European Heart Network, 2017.
-
- Townsend N, Wilson L, Bhatnagar P, et al. Cardiovascular disease in Europe: epidemiological update 2016. Eur Heart J 2016; 37: 3232–3245. - PubMed
-
- Feigin VL, Lawes CM, Bennett DA, et al. Worldwide stroke incidence and early case fatality reported in 56 population-based studies: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol 2009; 8: 355–369. - PubMed
-
- Heuschmann PU, Wiedmann S, Wellwood I, et al. Three-month stroke outcome: the European Registers of Stroke (EROS) investigators. Neurology 2011; 76: 159–165. - PubMed
-
- Truelsen T, Piechowski-Jozwiak B, Bonita R, et al. Stroke incidence and prevalence in Europe: a review of available data. Eur J Neurol 2006; 13: 581–598. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

