Indirect Effects of Early Parenting on Adult Antisocial Outcomes via Adolescent Conduct Disorder Symptoms and Callous-Unemotional Traits
- PMID: 31166154
- PMCID: PMC6893105
- DOI: 10.1080/15374416.2019.1613999
Indirect Effects of Early Parenting on Adult Antisocial Outcomes via Adolescent Conduct Disorder Symptoms and Callous-Unemotional Traits
Abstract
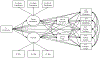
Parental harsh punishment and warmth have been associated with child and adolescent conduct disorder (CD) symptoms and callous-unemotional (CU) traits (i.e., lack of guilt, empathy, and deficient affect); however, it is unclear whether the effect of these parenting behaviors on antisocial outcomes persists into adulthood. Thus, the present study aimed to test whether adolescent CD symptoms and CU traits mediate the effect of parental harsh punishment and warmth on adult antisocial outcomes (i.e., antisocial personality disorder (ASPD), externalizing psychopathology, partner violence, and violent and substance crime). Participants included the high-risk control and normative samples from the Fast Track project (N =753, male = 58%, African American = 46%). Harsh punishment during kindergarten through grades 1-2 predicted higher adolescent CD symptoms, and directly observed warmth during kindergarten through grades 1-2 predicted lower adolescent CU traits. Adolescent CD symptoms predicted greater adult substance crime, and adolescent CU traits predicted greater adult ASPD symptoms and externalizing psychopathology. Further, adolescent CD symptoms indirectly accounted for the effect of parental harsh punishment on adult substance crime, and adolescent CU traits indirectly accounted for the effect of parental warmth on ASPD symptoms and externalizing psychopathology. Findings support the importance of early interventions targeting parenting behaviors to reduce risk for the development of antisocial behavior, and inform developmental models of antisocial behavior in adolescence through adulthood.
Figures
References
-
- Achenbach TM (1991). Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
-
- Achenbach TM (1997). Manual for the Young Adult Self-Report and Young Adult Behavior Checklist. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing.
-
- Barker ED, Oliver BR, Viding E, Salekin RT, & Maughan B (2011). The impact of prenatal maternal risk, fearless temperament and early parenting on adolescent callous-unemotional traits: A 14-year longitudinal investigation. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 52, 878–888. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2011.02397.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH062988/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R18 MH050951/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA016903/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R18 MH048043/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R18 MH050953/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 DA028248/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD093651/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DA023026/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K05 MH000797/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K05 DA015226/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K05 MH001027/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R18 MH050952/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
