Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for plaque psoriasis - Brazilian Society of Dermatology
- PMID: 31166402
- PMCID: PMC6544036
- DOI: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.2019940211
Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for plaque psoriasis - Brazilian Society of Dermatology
Abstract
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects 1.3% of the Brazilian population. The most common clinical manifestations are erythematous, scaling lesions that affect both genders and can occur on any anatomical site, preferentially involving the knees, elbows, scalp and genitals. Besides the impact on the quality of life, the systemic nature of the disease makes psoriasis an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease, especially in young patients with severe disease. By an initiative of the Brazilian Society of Dermatology, dermatologists with renowned clinical experience in the management of psoriasis were invited to form a work group that, in a partnership with the Brazilian Medical Association, dedicated themselves to create the Plaque Psoriasis Diagnostic and Treatment Guidelines. The relevant issues for the diagnosis (evaluation of severity and comorbidities) and treatment of plaque psoriasis were defined. The issues generated a search strategy in the Medline-PubMed database up to July 2018. Subsequently, the answers to the questions of the recommendations were devised, and each reference selected presented the respective level of recommendation and strength of scientific evidence. The final recommendations for making up the final text were worded by the coordinators.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The coauthors hereby declare that they participated in meetings and talks and/or received support from the following pharmaceutical laboratories: Marcelo Arnone: Abbvie, Glenmark, Janssen, Leo Pharma, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Biopharma; Maria Denise Fonseca Takahashi: Abbvie, Janssen, and Pfizer; André Vicente Esteves de Carvalho: Abbvie, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, and UCB; Biopharma; Wanderley Marques Bernardo: none; Aline Lopes Bressan: Abbvie; Andréa Machado Coelho Ramos: Abbvie, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Sanofi, and UCB; Biopharma; Aripuana Cobério Terena: Abbvie, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, and Sanofi; Cacilda da Silva Souza: Abbvie, Janssen, Leo Pharma, Lilly, and Novartis; Daniel Holthausen Nunes: Abbvie, Janssen, Novartis, and Sanofi; Maria Cecília de Carvalho Bortoletto: Abbvie, Janssen, and Novartis; Maria de Fátima Santos Paim de Oliveira: Abbvie, Janssen, Leo Pharma, and Novartis; Jane Marcy Neffá: Abbvie and Pfizer; Luciana Cristina Fieri: none; Luna Azulay-Abulafia: Abbvie, Janssen, Leo Pharma, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche; Paulo Antônio Oldani Felix: Abbvie, Astra-Zeneca, Janssen, Leo Pharma, Lilly, Novartis, UCB Biopharma; Renata Ferreira Magalhaes: Abbvie, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, and Pfizer Ricardo Romiti: Abbvie, Galderma, Janssen, Leo Pharma, Lilly, Novartis, Sanofi, and UCB Biopharma; Tatiana Jerez Jaime: none
Figures
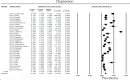
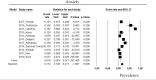




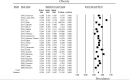



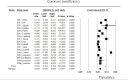

References
-
- Arnone M, Carvalho AVE, Takahashi MDF, Bernardo WM, et al. Projeto Diretrizes AMB: Psoríase. [2018 dec 14]. Available from: http://diretrizes.amb.org.br/?s=psoriase.
-
- Aktan S, Ilknur T, Akin C, Ozkan S. Interobserver reliability of the Nail Psoriasis Severity Index. Clin Exp Dermatol. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2007;32:141–144. - PubMed
-
- Bronsard V, Paul C, Prey S, Puzenat E, Gourraud PA, Aractingi S, et al. What are the best outcome measures for assessing quality of life in plaque type psoriasis? A systematic review of the literature. JJ Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010;24(Suppl 2):S17–S22. - PubMed
-
- Chularojanamontri L, Griffiths CE, Chalmers RJ. The Simplified Psoriasis Index (SPI): A Practical Tool for Assessing Psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:1956–1962. - PubMed
-
- Gottlieb AB, Merola JF, Chen R, Levi E, Duffin KC. Assessing clinical response and defining minimal disease activity in plaque psoriasis with the Physician Global Assessment and body surface area (PGA × BSA) composite tool: An analysis of apremilast phase 3 ESTEEM data. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:1178–1180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

