Reduced Cortical Thickness in Schizophrenia and Schizotypal Disorder
- PMID: 31167030
- PMCID: PMC7406196
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbz051
Reduced Cortical Thickness in Schizophrenia and Schizotypal Disorder
Abstract
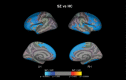
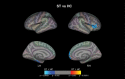
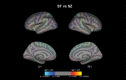
Schizotypal disorder is characterized by odd behavior and attenuated forms of schizophrenic features without the manifestation of overt and sustained psychoses. Past studies suggest that schizotypal disorder shares biological and psychological commonalties with schizophrenia. Structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies have demonstrated both common and distinct regional gray matter changes between schizophrenia and schizotypal disorder. However, no study has compared cortical thickness, which is thought to be a specific indicator of cortical atrophy, between schizophrenia and schizotypal disorder. The subjects consisted of 102 schizophrenia and 46 schizotypal disorder patients who met the International Classification of Diseases, 10th edition criteria and 79 gender- and age-matched healthy controls. Each participant underwent a T1-weighted 3-D MRI scan using a 1.5-Tesla scanner. Cortical thickness was estimated using FreeSurfer. Consistent with previous studies, schizophrenia patients exhibited wide-spread cortical thinning predominantly in the frontal and temporal regions as compared with healthy subjects. Patients with schizotypal disorder had a significantly reduced cortical thickness in the left fusiform and parahippocampal gyri, right medial superior frontal gyrus, right inferior frontal gyrus, and right medial orbitofrontal cortex as compared with healthy controls. Schizophrenia patients had thinner cortices in the left precentral and paracentral gyri than those with schizotypal disorder. Common cortical thinning patterns observed in schizophrenia and schizotypal disorder patients may be associated with vulnerability to psychosis. Our results also suggest that distinct cortical changes in schizophrenia and schizotypal disorder may be associated with the differences in the manifestation of clinical symptoms among these disorders.
Keywords: cortical thickness; magnetic resonance imaging; schizophrenia; schizophrenia spectrum; schizotypal disorder.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders: Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 1992.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed. (DSM-IV). Washington, DC: APA; 1994.
-
- Siever LJ, Kalus OF, Keefe RS. The boundaries of schizophrenia. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 1993;16(2):217–244. - PubMed
-
- Siever LJ, Davis KL. The pathophysiology of schizophrenia disorders: perspectives from the spectrum. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161(3):398–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

